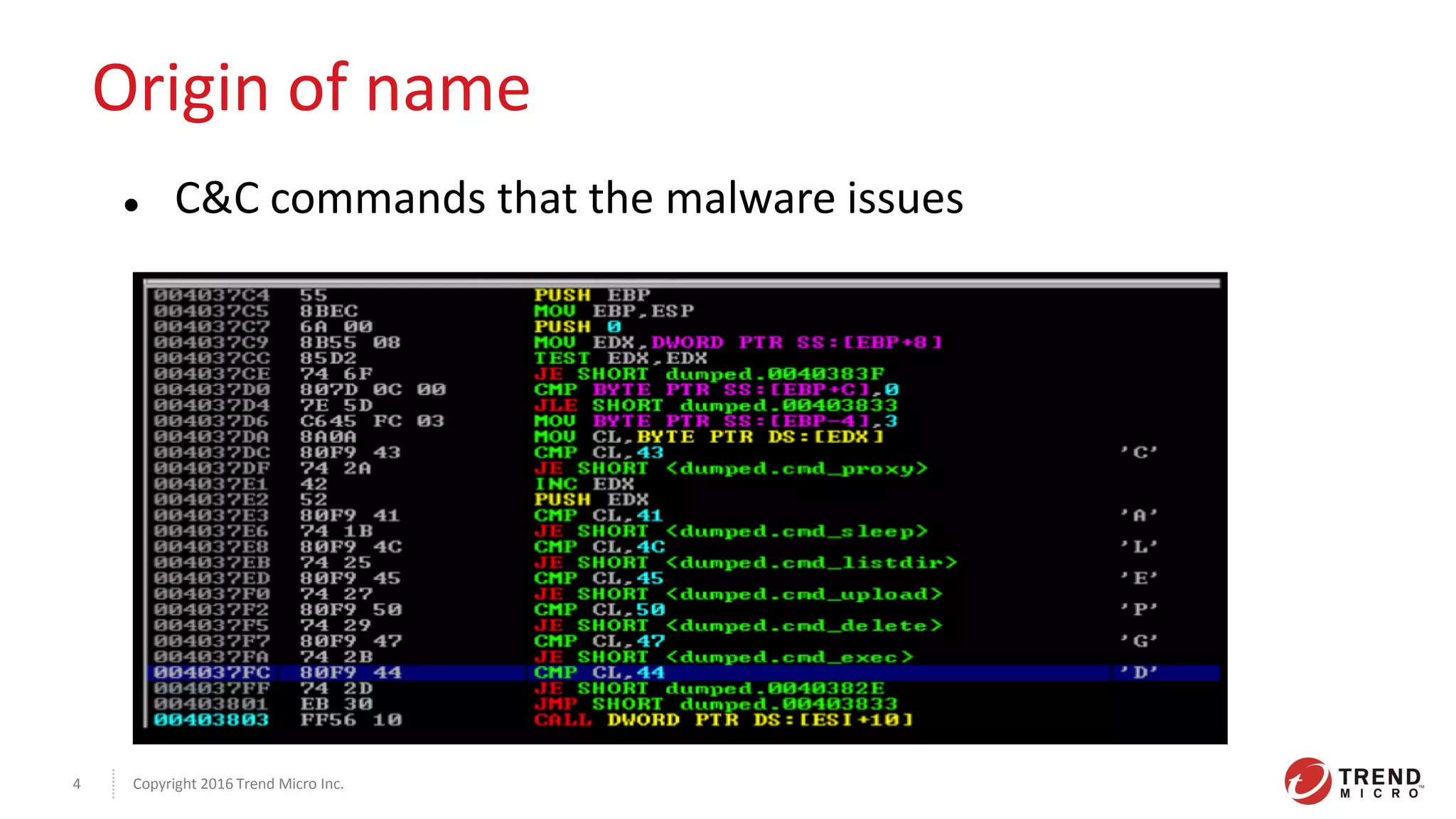
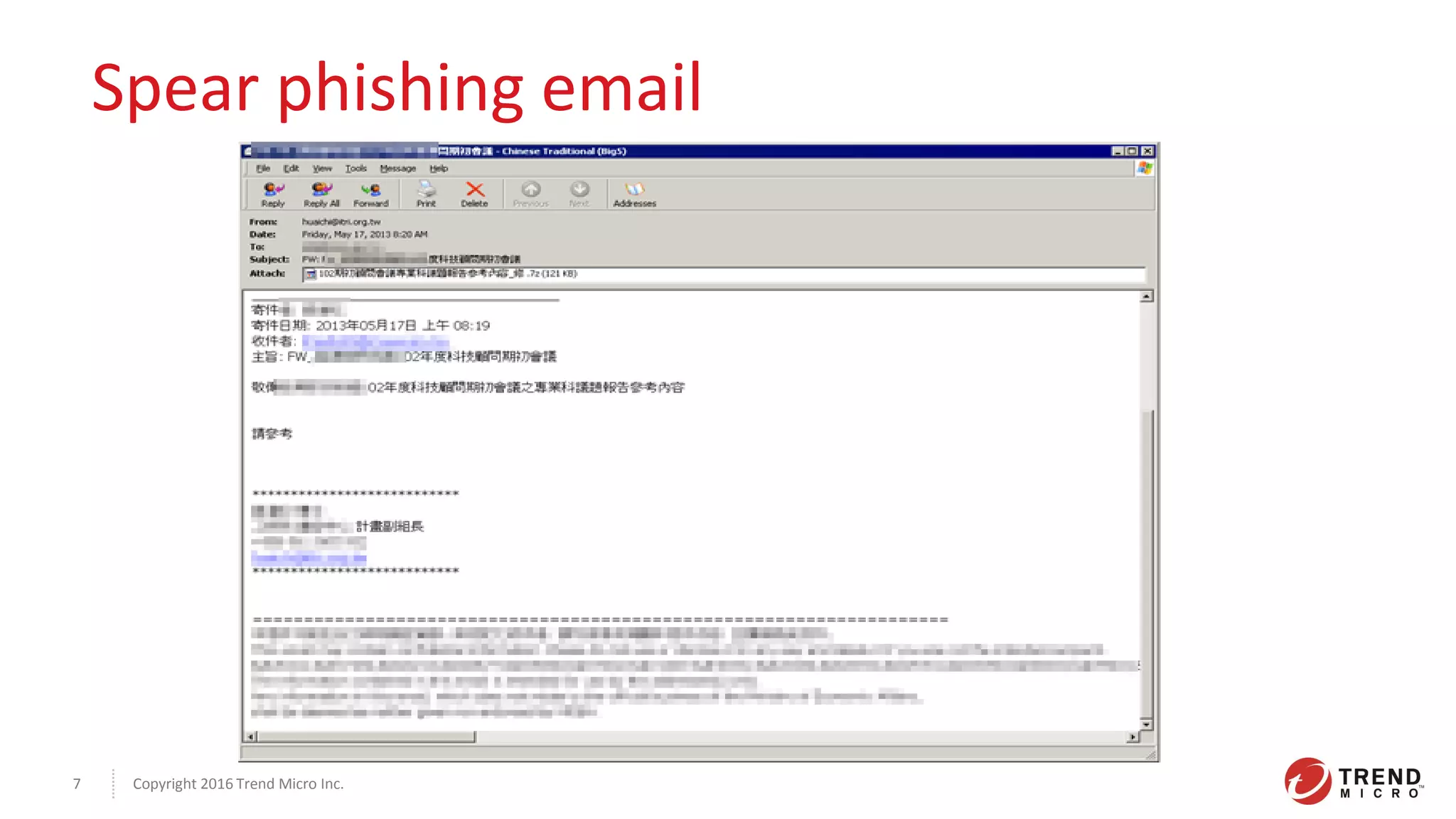
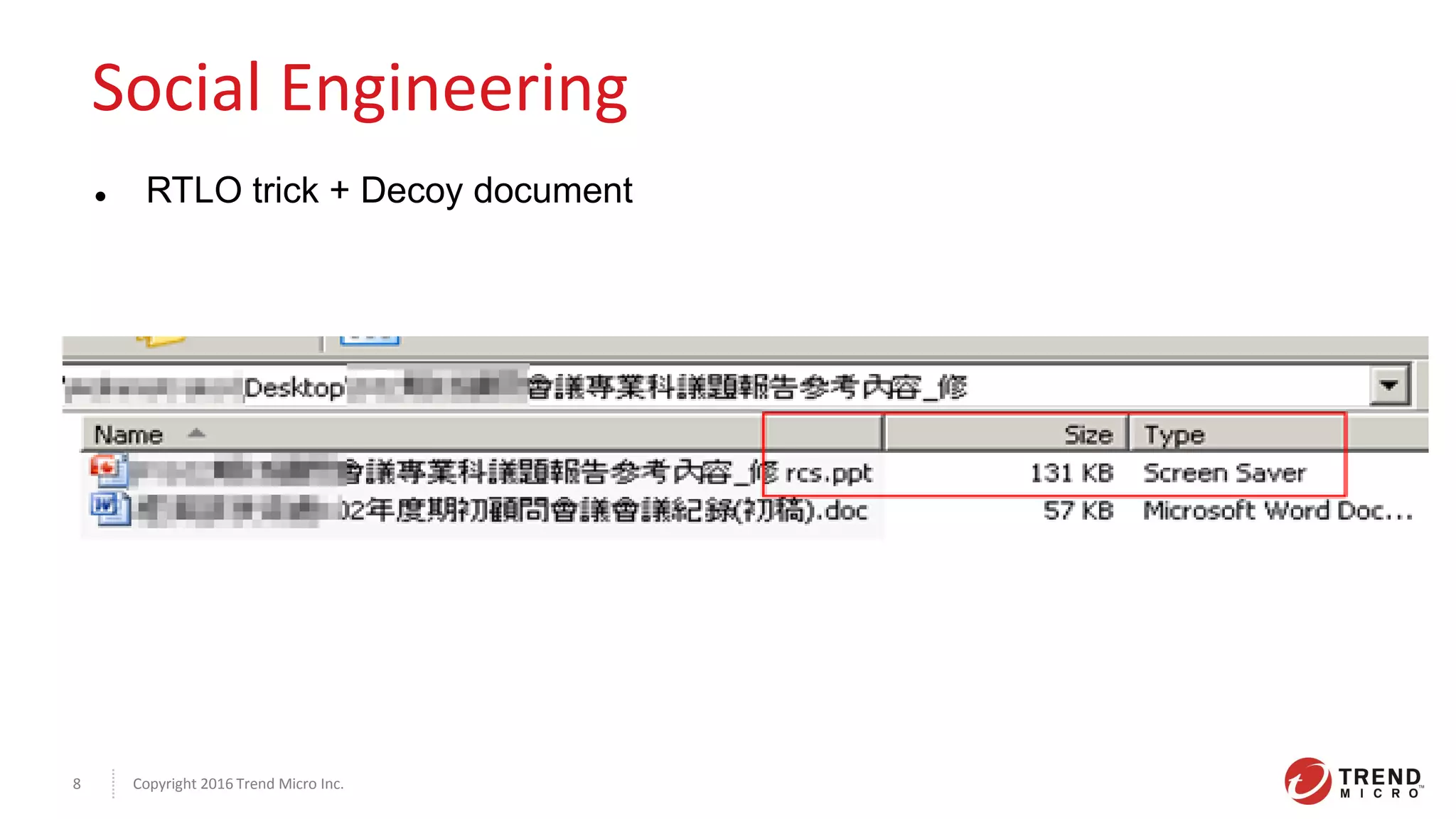
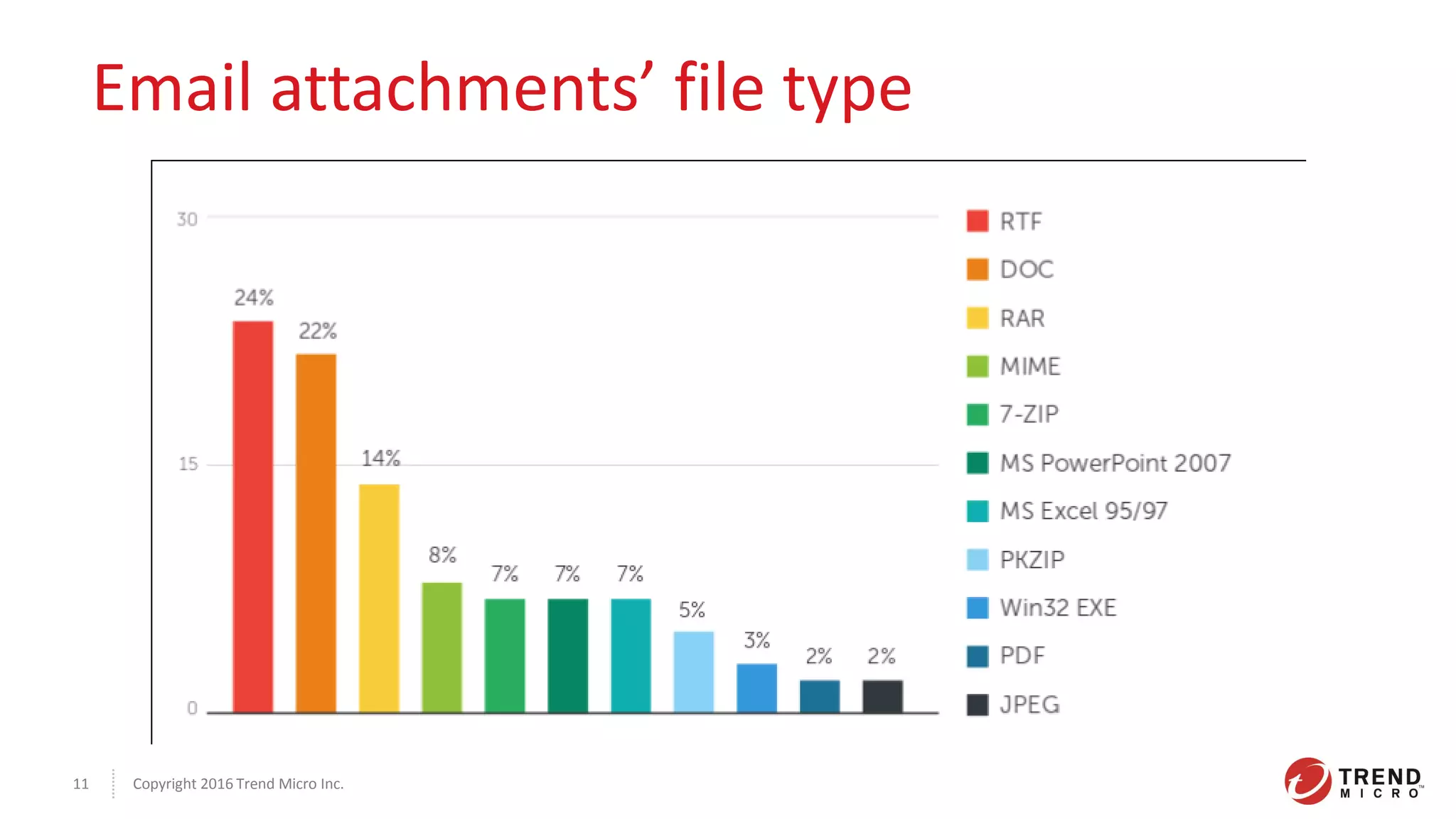
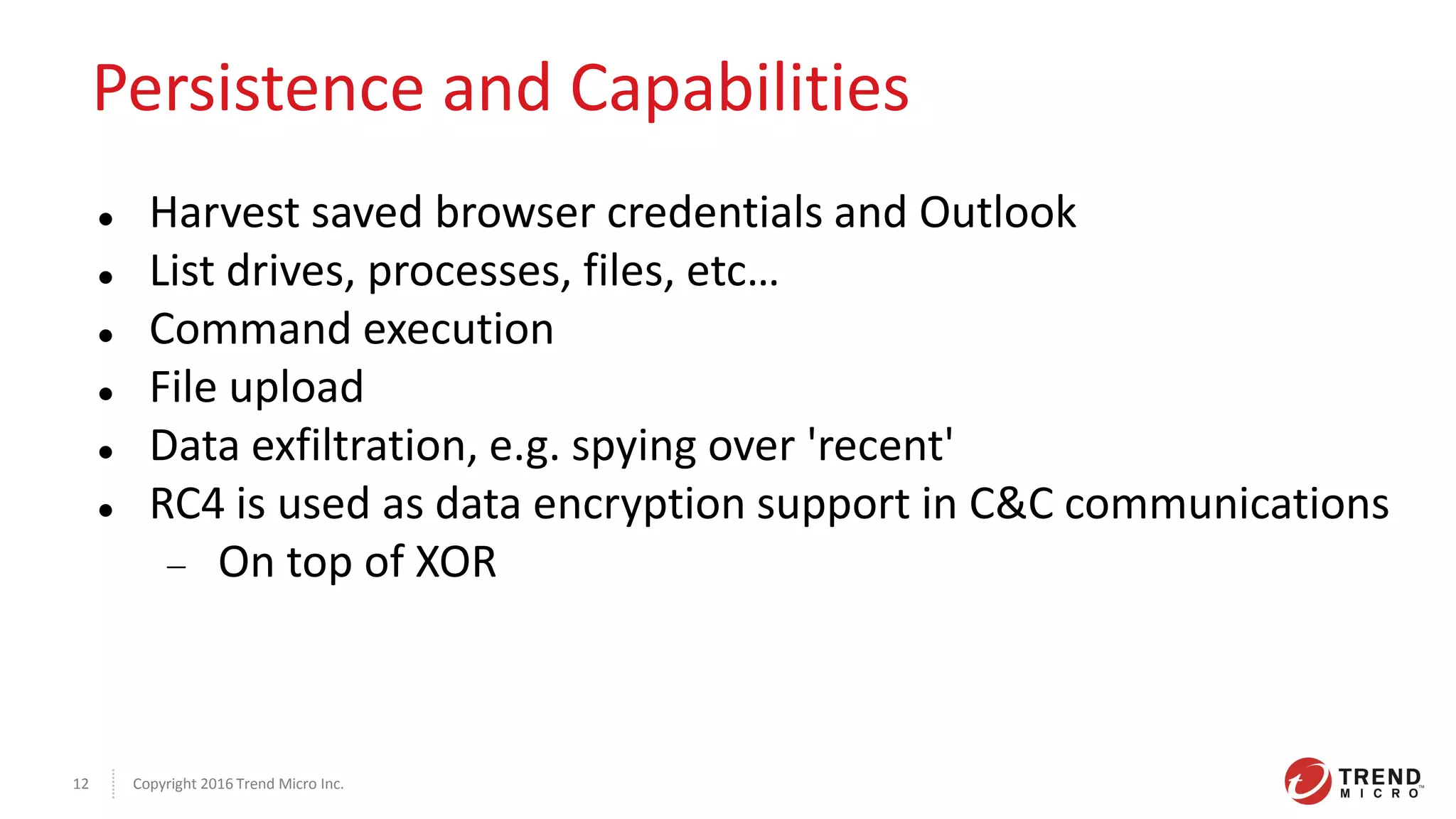
This document discusses the Plead APT, which has targeted Taiwanese government and industry organizations since 2012 through spear phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links. The attacks utilized exploits like Flash zero-days and Microsoft Word vulnerabilities to compromise victims and establish persistence through credential harvesting and command execution. Stolen data was exfiltrated using tools like DRIGO to synchronize with Google Drive in a stealthy manner. The attacks demonstrate the multi-stage nature of advanced threats and importance of threat intelligence and defense-in-depth protections against sophisticated adversaries.