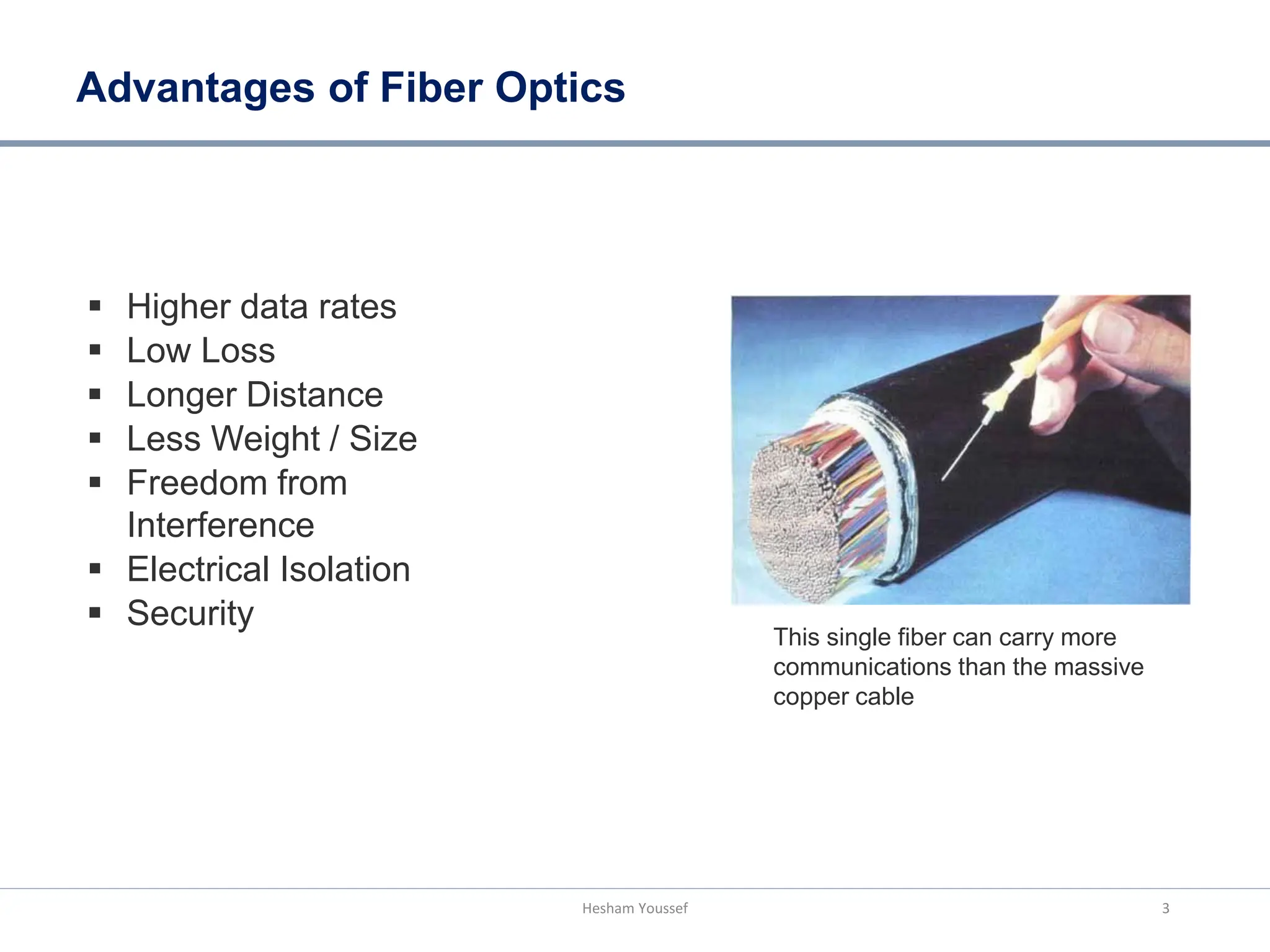
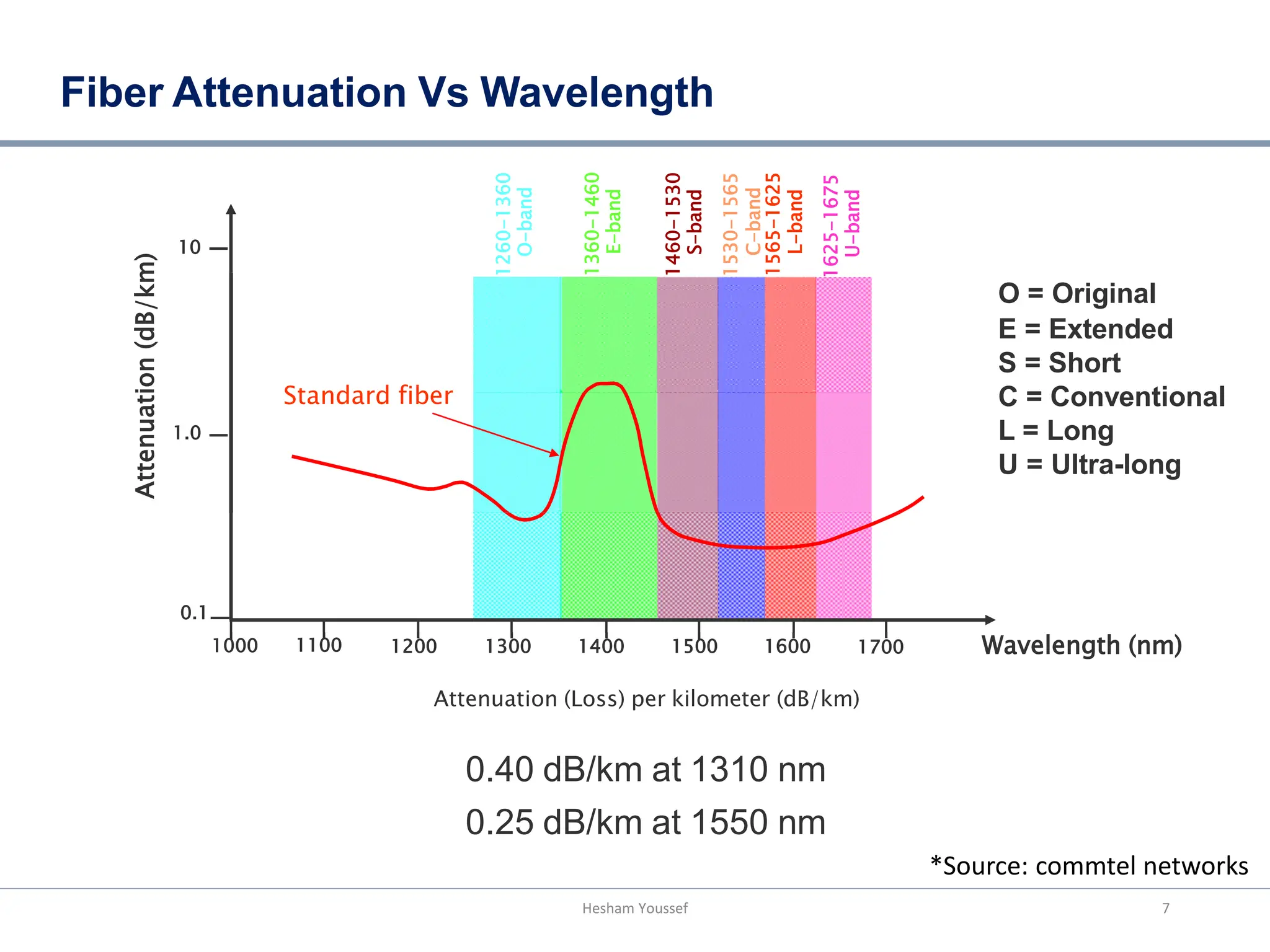
Fiber optic transmission uses glass or plastic fibers to transmit pulses of infrared light over long or short distances, carrying large amounts of data. It has several advantages over copper cable transmission such as higher data rates, lower loss over longer distances, less weight and size, immunity to electromagnetic interference, electrical isolation, and greater security. As data traffic has increased dramatically since the 1990s, options to increase bandwidth include installing more fibers, increasing transmission bit rates using faster electronics, or using wavelength division multiplexing to transmit multiple signals simultaneously on the same fiber at different wavelengths. WDM technology has helped fiber optic networks scale their capacity over decades to meet explosive growth in data usage.





![Evolution of transmission capacity
8
[P. Winzer et al., IEEE JLT, Dec. 2012]
Hesham Youssef](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plc3-231107111728-284adc24/75/PLC3-pdf-8-2048.jpg)