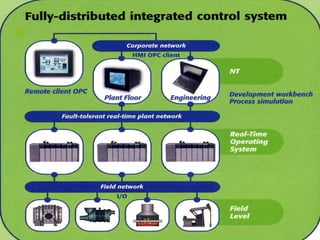
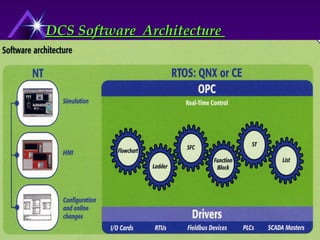
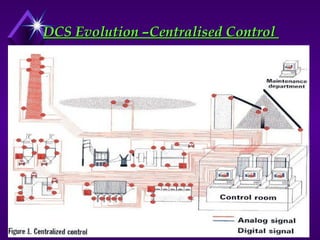
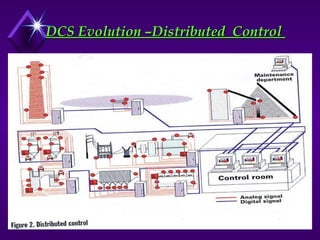
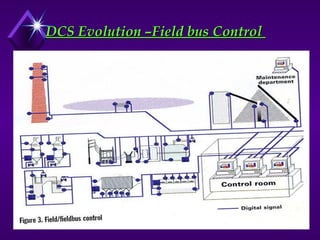
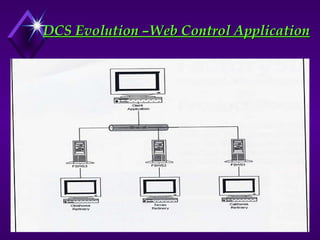
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) defines PLC as a digital electronic device that uses a programmable memory to store instructions and to implement specific functions such as logic, sequence, timing, counting, and arithmetic operations to control machines and processes.
The PLC is an assembly of solid-state digital logic elements designed to make logical decisions and provide outputs.
PLC is a programmed interface between input sensors & output devices.