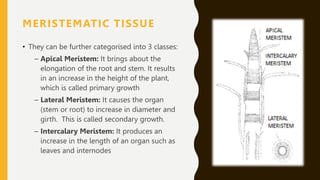
This document discusses the different types of plant tissues. It explains that there are two main types: meristematic tissue and permanent tissue. Meristematic tissue includes apical, lateral and intercalary meristems which allow for growth. Permanent tissues are fully developed and include two types - simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, and complex tissues such as xylem and phloem which transport water and nutrients. Each tissue is then defined and their functions described.