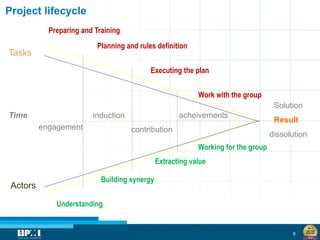
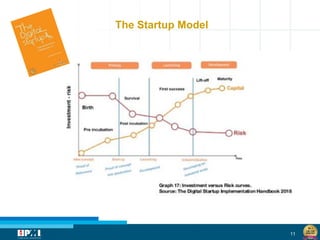
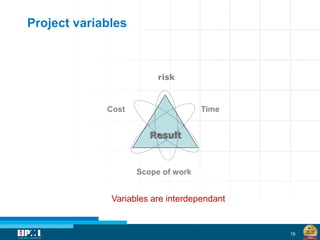
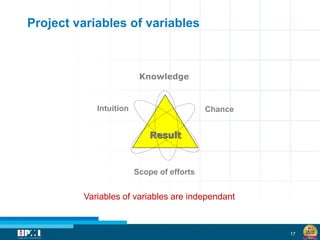
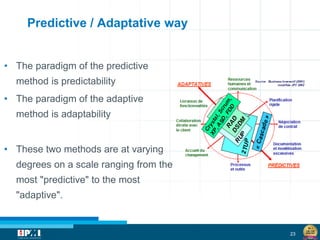
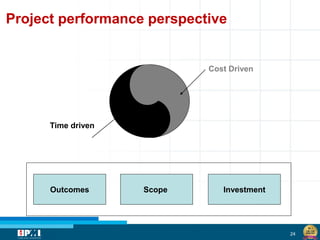
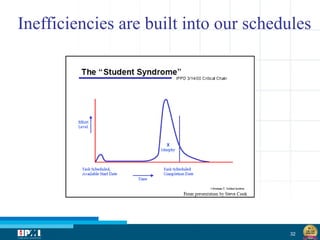
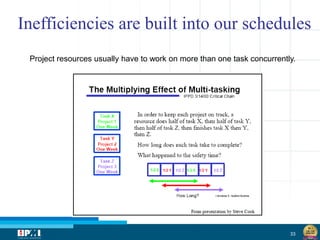
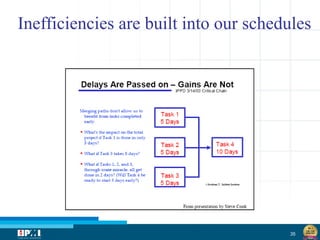
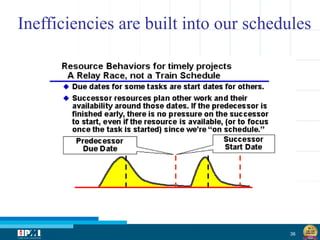
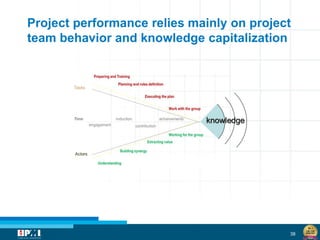
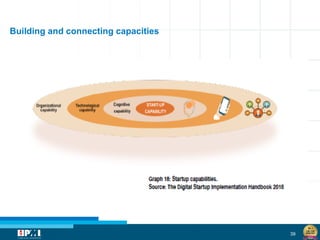
The document discusses a startup model for project management in high uncertainty contexts, emphasizing the challenges of planning innovation projects. It highlights the importance of adaptability and managing paradoxes in planning to enhance project outcomes and performance. Key insights include the need for effective team behavior, risk anticipation, and balancing various project variables.