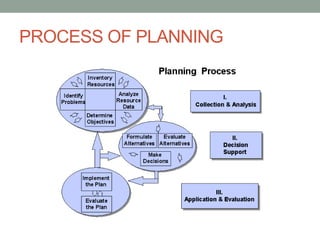
This document discusses planning in management. It defines planning as deciding in advance what is to be done, when, where, how, and by whom. Planning bridges the gap from the present to desired future goals. The document outlines the types of planning as corporate, functional, and operational based on scope and time period. It also discusses the purposes, nature, advantages, and process of planning.