This document provides information on Singapore, including:
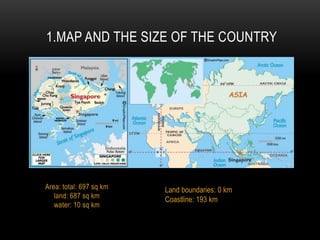
1) Singapore is an island country with a population of over 5 million located in Southeast Asia. English is the primary language though Malay is the national language.
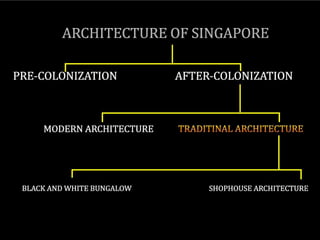
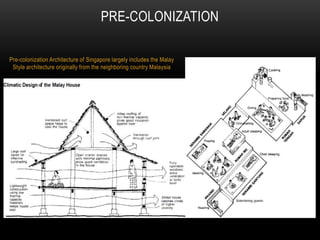
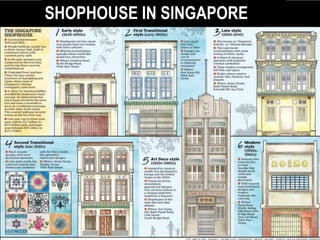
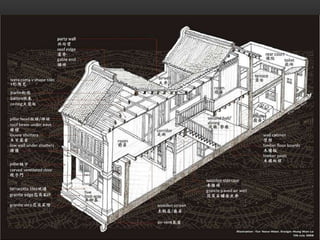
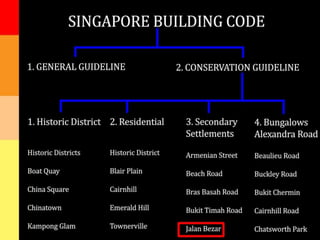
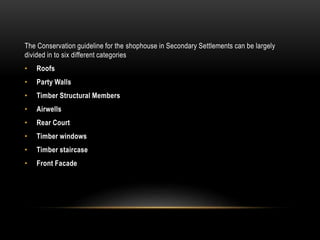
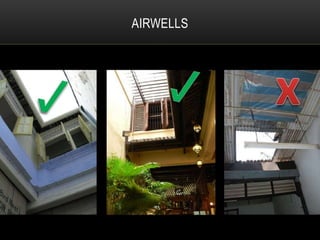
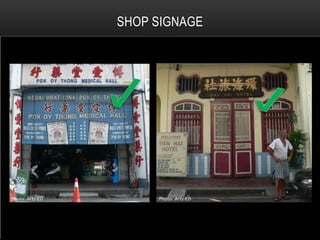
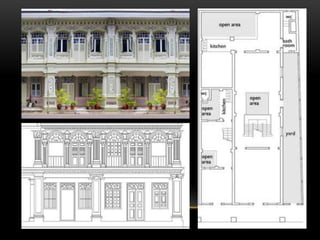
2) The architecture of Singapore has traditionally included shophouses, which are two to three story buildings with shops on the ground floor and residences above. Conservation guidelines aim to preserve features like roofs, party walls, and timber elements.
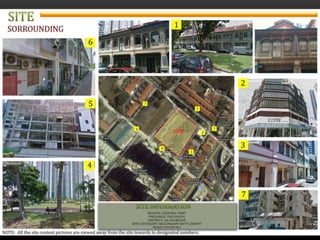
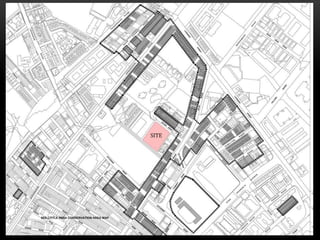
3) The proposed site for development lies on a historic street featuring a variety of shophouse styles, offering an opportunity to contribute to the culturally and architecturally rich area through a new project.