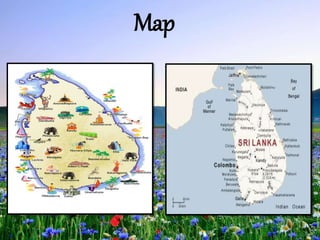
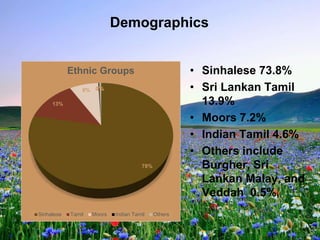
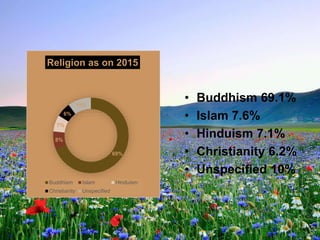
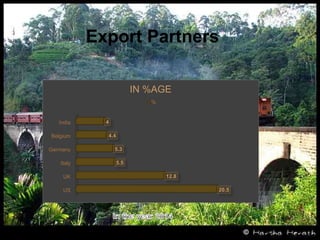
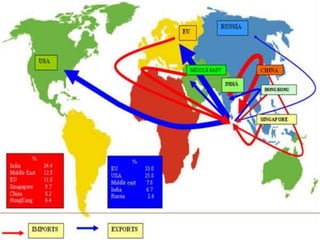
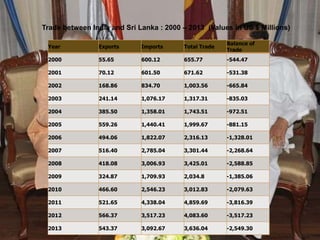
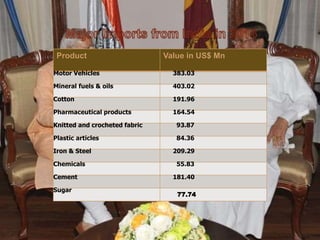
Sri Lanka is an island country located off the southeast coast of India. It has a population of over 21 million people and its capital and largest city is Colombo. The main ethnic groups are Sinhalese, Sri Lankan Tamil, Moors, and Indian Tamil. Buddhism is the largest religion. Sri Lanka has a developing economy based around agriculture, fishing, and tourism. It has close economic and political ties to India and China. The presentation provided an overview of Sri Lanka's geography, culture, politics, economy and trade relationships.