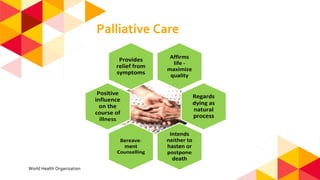
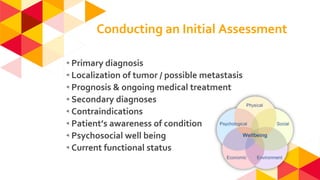
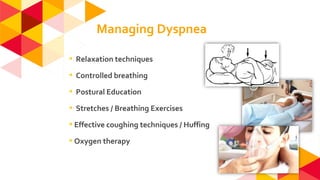
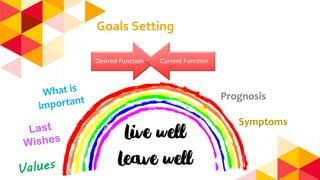
The document outlines the role of physiotherapy in palliative care, focusing on improving the quality of life for patients facing life-threatening illnesses by managing physical, psychosocial, and spiritual issues. Key responsibilities include promoting physical activity, managing symptoms, and training caregivers, alongside initial assessments of patients' conditions. It emphasizes the importance of communication and collaboration among multidisciplinary teams to enhance care delivery.