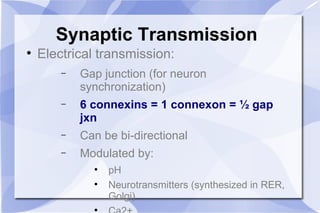
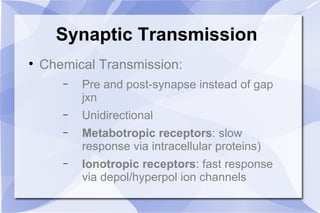
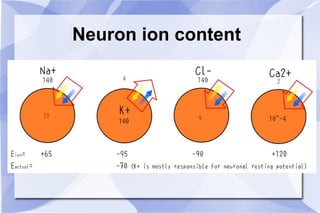
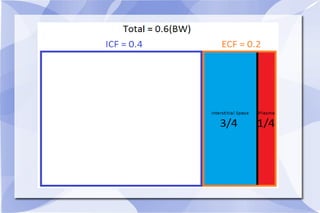
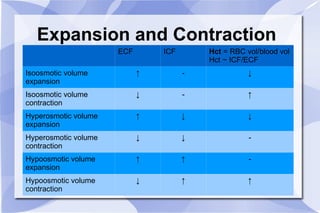
This document summarizes key concepts related to body fluid compartments, osmotic pressure, and synaptic transmission in physiology. It discusses that total body water is 60% of body weight, with intracellular fluid making up 40% and extracellular fluid 20%. Extracellular fluid is further divided into interstitial and plasma sub-compartments. Osmotic pressure is determined by effective osmolytes that cannot cross cell membranes. Synaptic transmission can occur electrically through gap junctions or chemically through neurotransmitters acting on ionotropic or metabotropic receptors. Action potentials are generated by the opening and closing of sodium and potassium ion channels in neurons.

![Contact us: Julie: [email_address] Jenesha: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physioweek1-100905234624-phpapp01/85/Physio1-Week-1-2-320.jpg)

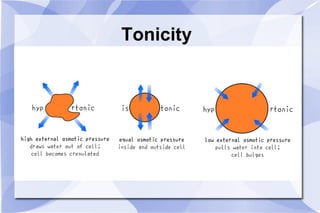

![π = σ(nCRT) π = Osmotic pressure σ = reflection coefficient (0-1) 0 = ineffective osmolyte 1 = impermeant N = dissociable particles C = total [solute] R = gas constant T = Kelvin Determining Tonicity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physioweek1-100905234624-phpapp01/85/Physio1-Week-1-8-320.jpg)