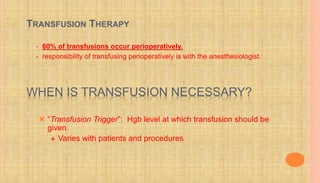
This document discusses goal-directed fluid therapy and summarizes key points about fluid management for various clinical situations. The main points are:
- Goal-directed therapy aims to optimize physiologic variables like cardiac output and oxygen delivery through fluid administration and inotropes/vasopressors to improve tissue perfusion and outcomes.
- Special populations like heart failure, kidney disease, sepsis, burns and liver disease require a delicate fluid balance to avoid complications from overhydration or underhydration.
- Fluid management in pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia must be conservative to prevent pulmonary edema given the clear association between positive fluid balance and this complication.


![TECHNIQUES USED FOR PERIOPERATIVE GDT:
Pulmonary artery catheter (PAC)
Gold standard hemodynamic monitor,
provides measured and derived values for Left and right heart filling pressures, mixed
and central venous saturations and CO.
Esophageal Doppler monitor (EDM)
ultrasound measurement of descending aorta blood velocity=> SV => CO
Partial CO2–rebreathing technique [noninvasive cardiac output (NICO)],
Lithium dilution [lithium dilution cardiac output (LiDCO)]
Plethysmography and
Gastric tonometry
Thoracic Bioimpedance (non-invasively measures SV & CO through 4 surface ECG
electrodes)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perioperativefluidtherapy-160516142225/85/Perioperative-fluid-therapy-3-320.jpg)

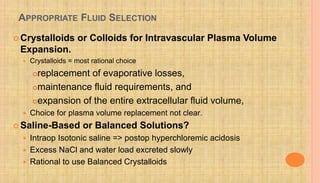











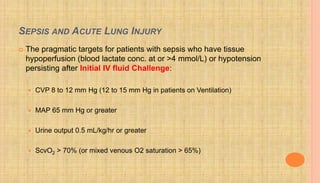



![HEPATIC FAILURE
Progressive liver disease and cirrhosis cause
peripheral vasodilation and
relative intravascular depletion (total body Na+ and water are retained with
ascites and edema )
Aim is reduction of total body salt and water
[dietary fluid and salt restriction, diuretics (spironolactone and loop diuretics),
and intermittent or continuous drainage of ascites]
Excessive isotonic saline => salt and water overload=> further ascites
and edema formation.
Approach => Assess volume status and replace losses with
appropriate volumes of isotonic crystalloid, colloid, or blood but avoid
salt and water overload.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perioperativefluidtherapy-160516142225/85/Perioperative-fluid-therapy-21-320.jpg)