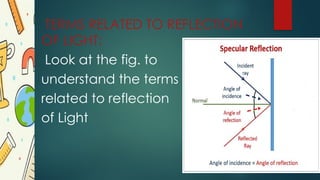
The document discusses the phenomenon of light reflection, explaining how mirrors create images through light reflection, with a focus on plane and spherical mirrors. It describes two types of reflection: regular reflection, occurring on smooth polished surfaces, and irregular (or diffused) reflection on rough surfaces. Additionally, it introduces key terms related to the reflection process, such as incident ray, reflected ray, and angles of incidence and reflection.