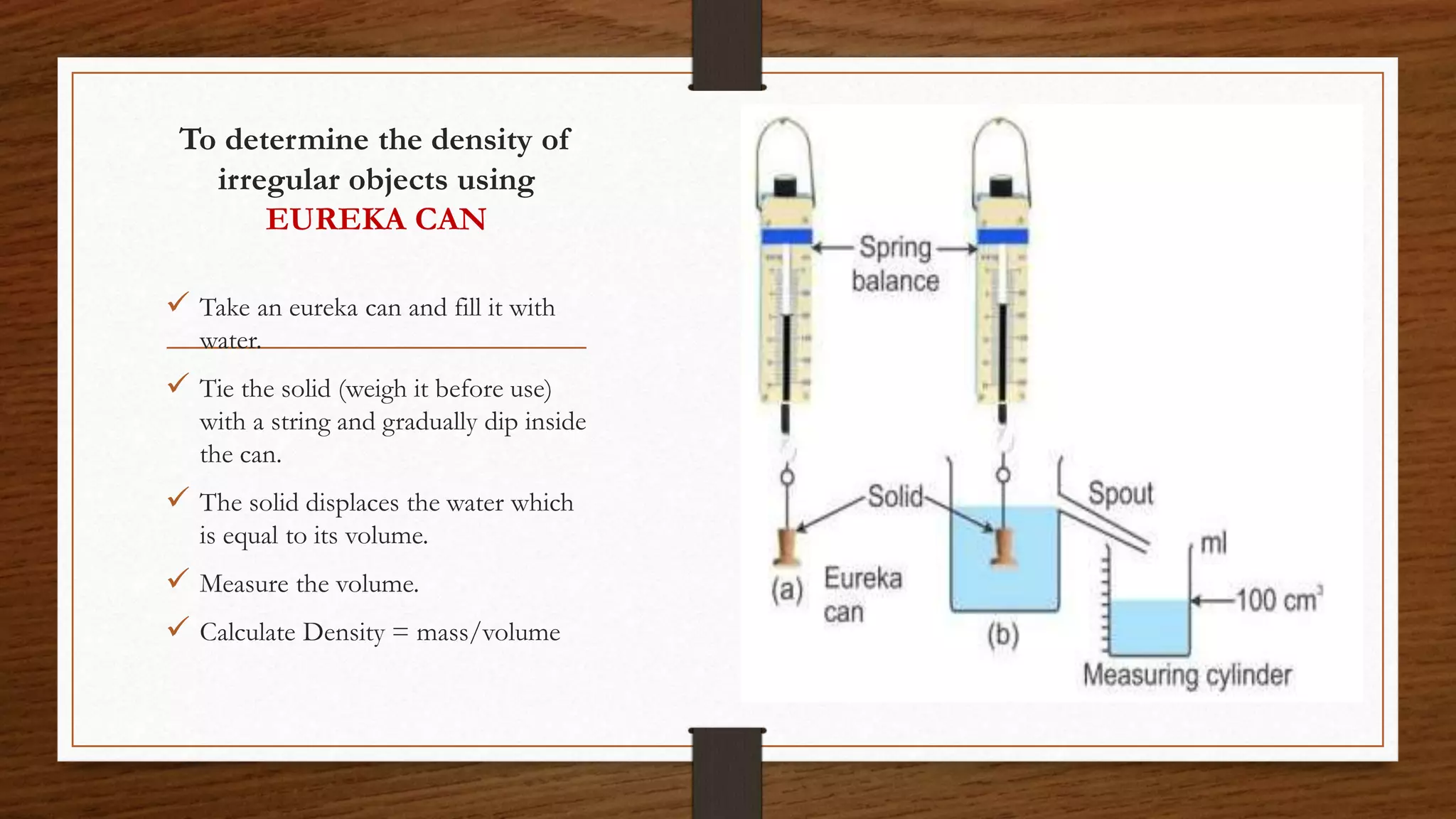
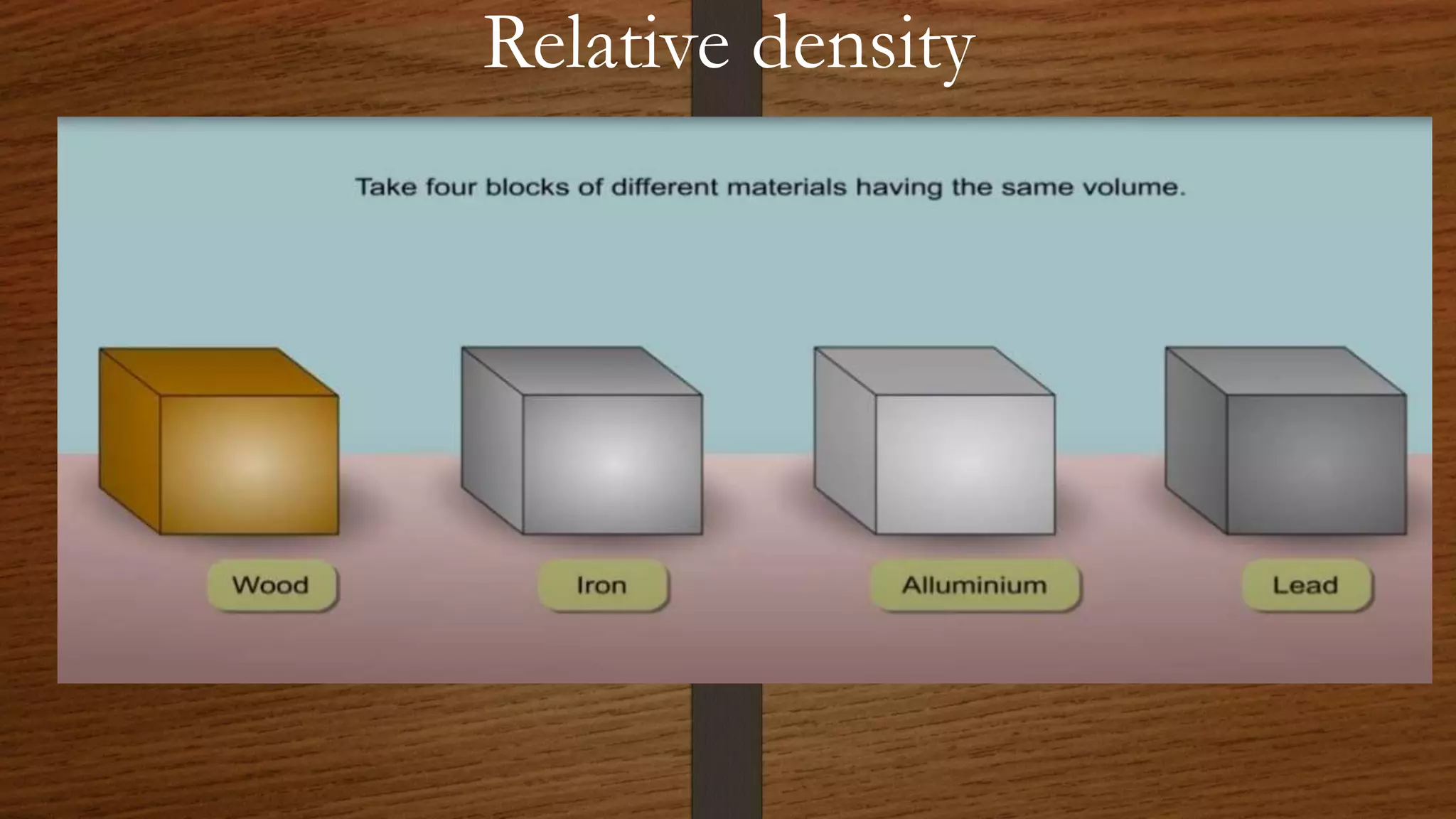
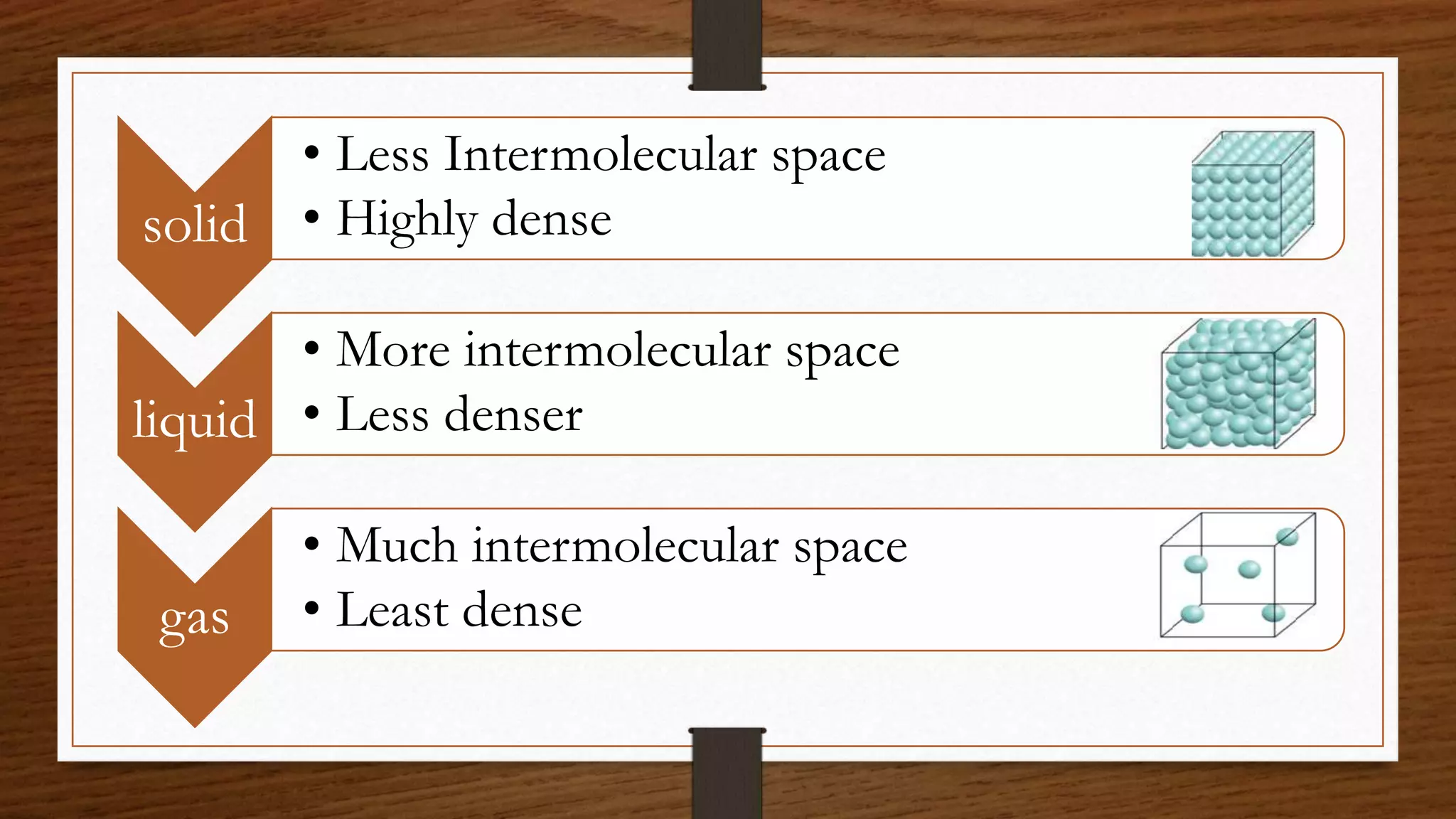
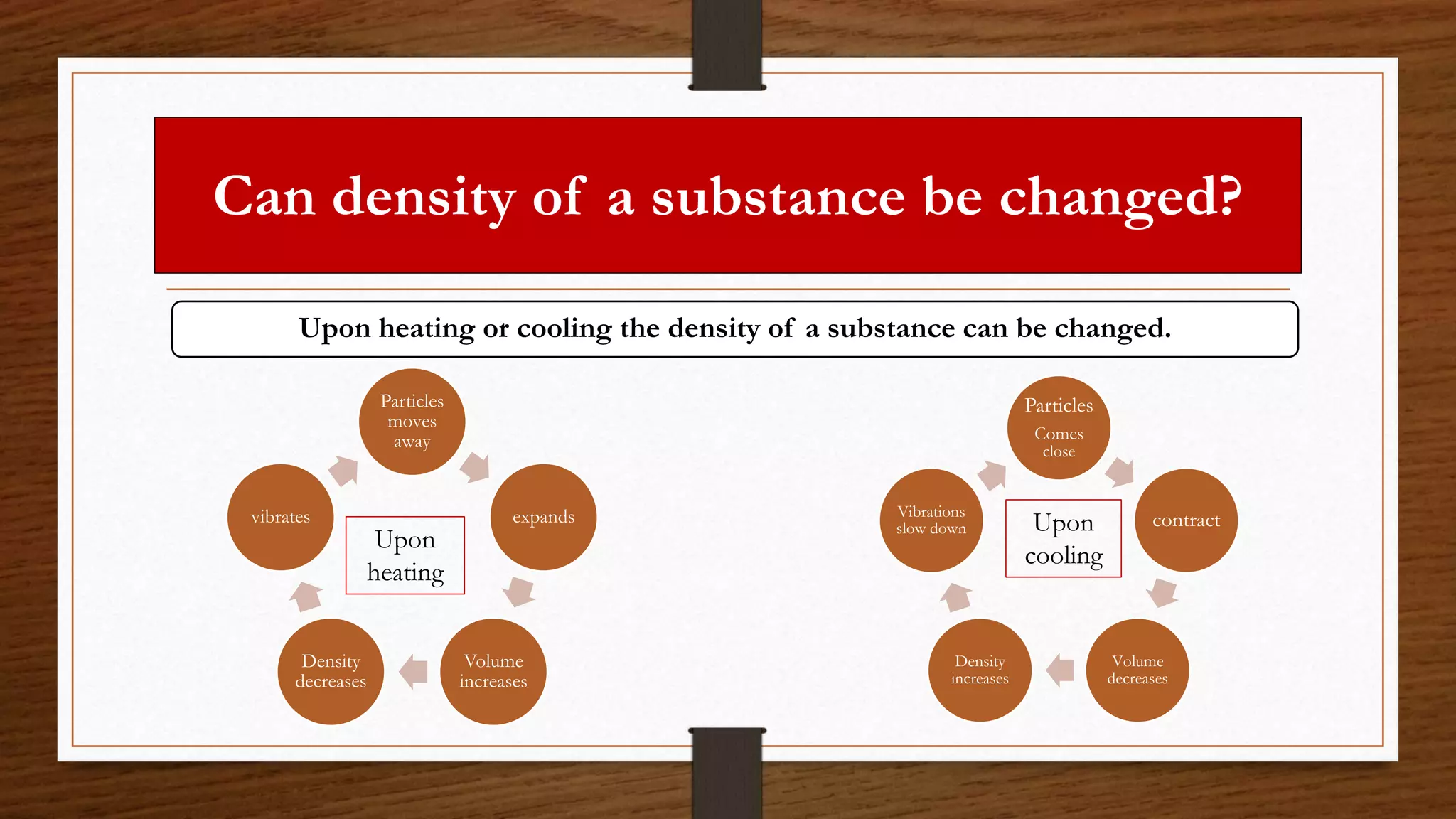
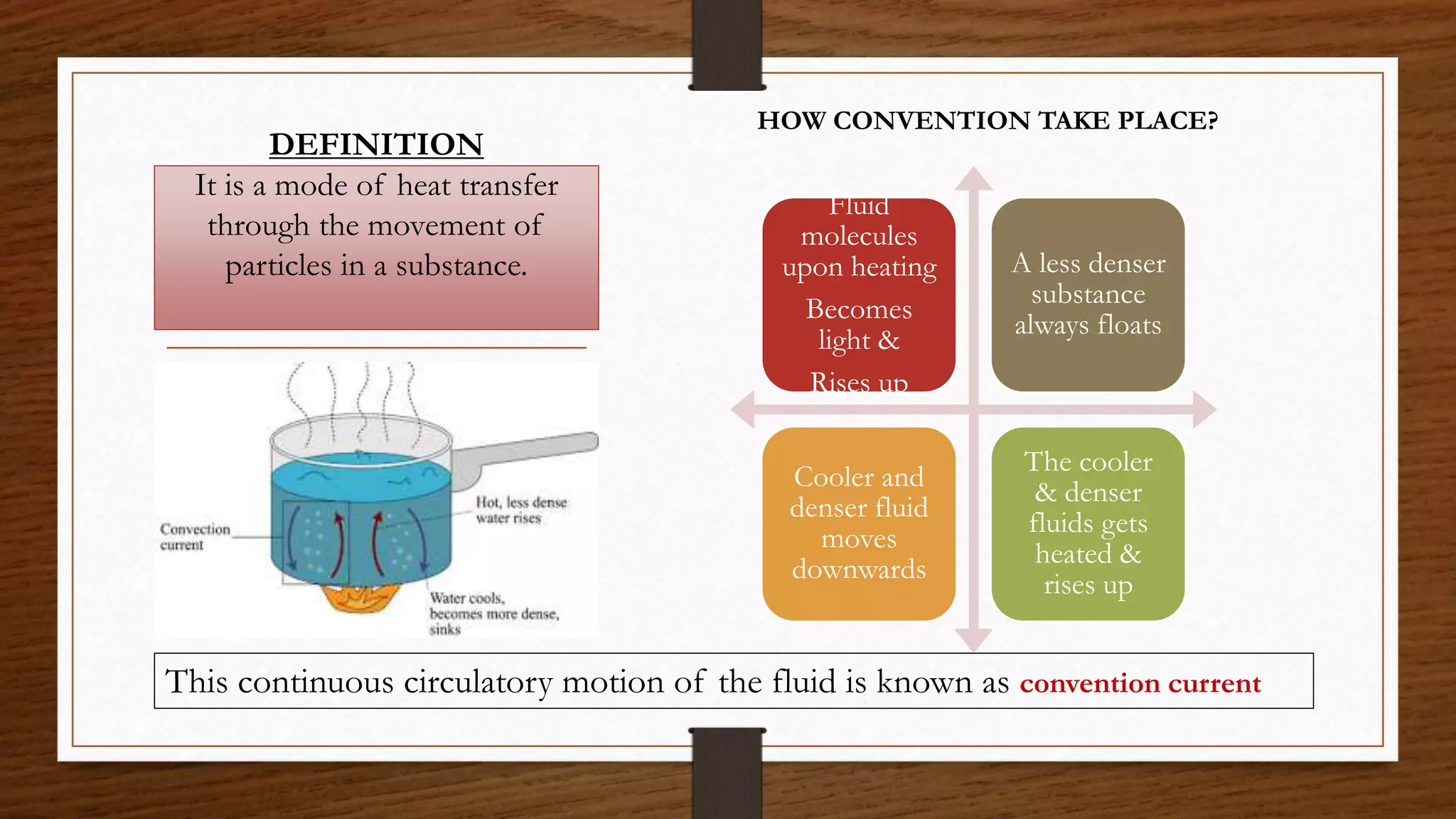
The document discusses the concepts of density and relative density, detailing their definitions, measurements, and applications in the context of physical quantities and measurement. It outlines experiments for determining density and understanding the principles of floating and sinking based on density differences across states of matter. The document also includes numerical problems and evaluation questions relevant to the concepts introduced.