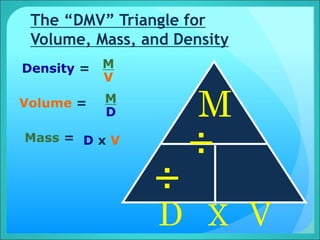
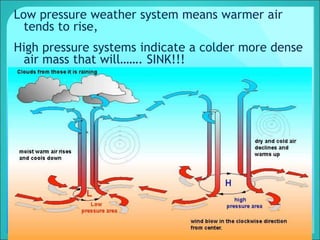
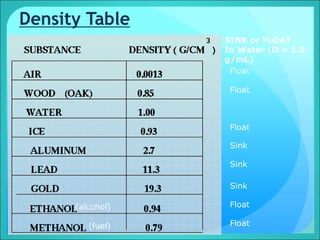
Density is a measure of the compactness of a substance and is calculated as mass divided by volume. It can be used to determine whether an object will sink or float in a liquid like water. Factors like temperature, pressure, and dissolved solids can impact the density of gases, liquids, and solids. Irregularly shaped objects have their density determined by first measuring their mass and then finding their volume by measuring the displacement of water.