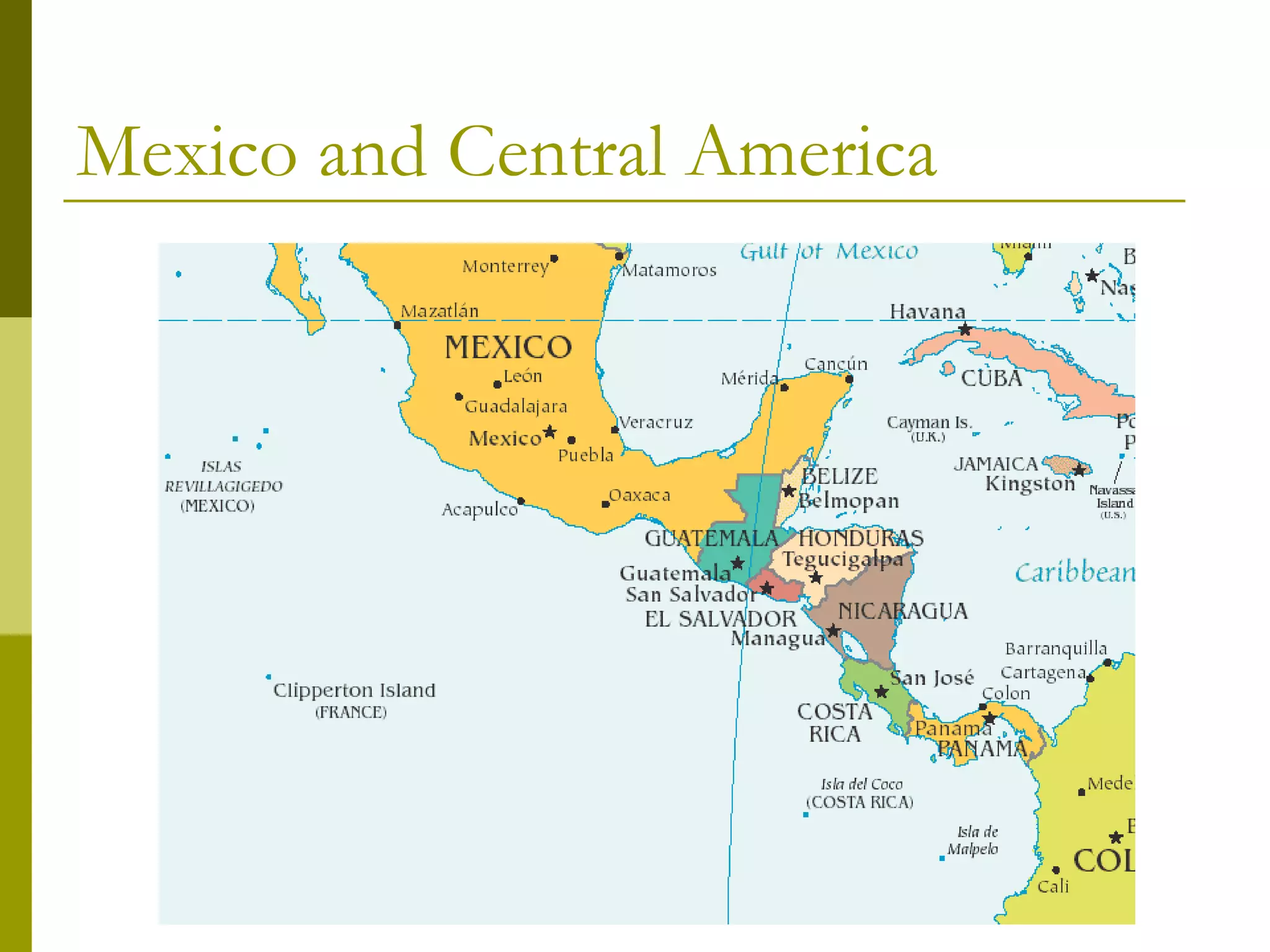
Latin America's physical geography is divided into three regions: Mexico and Central America, the Caribbean, and South America. Mexico and Central America feature mountain ranges like the Sierra Madre and a central plateau in Mexico. Central America is an isthmus connecting North and South America crossed by the important Panama Canal. The Caribbean islands vary in size from small coral islands to larger islands formed from underwater mountains. South America is dominated by the massive Andes Mountains along the western coast and the immense Amazon River Basin and rainforest in the center.