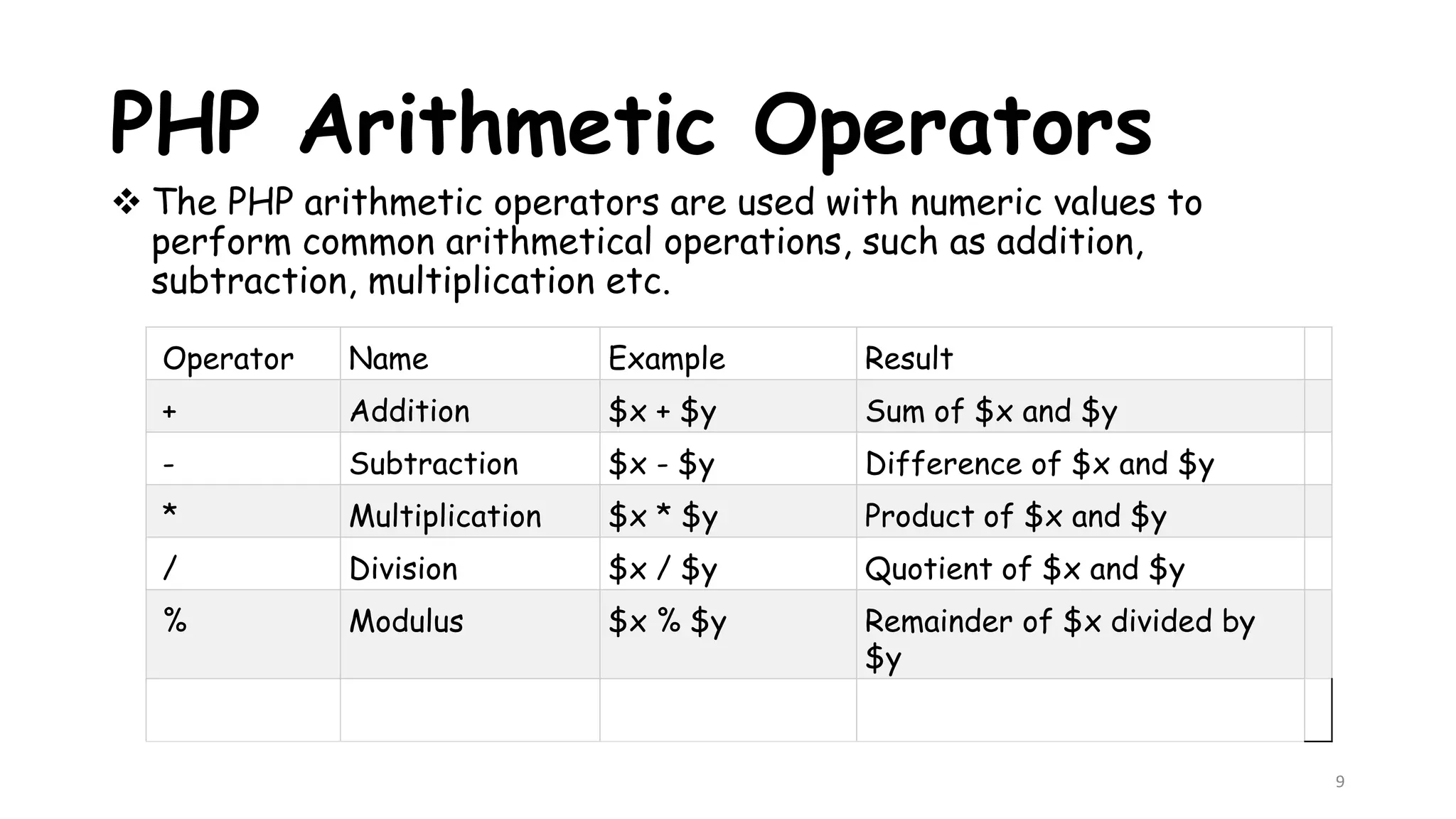
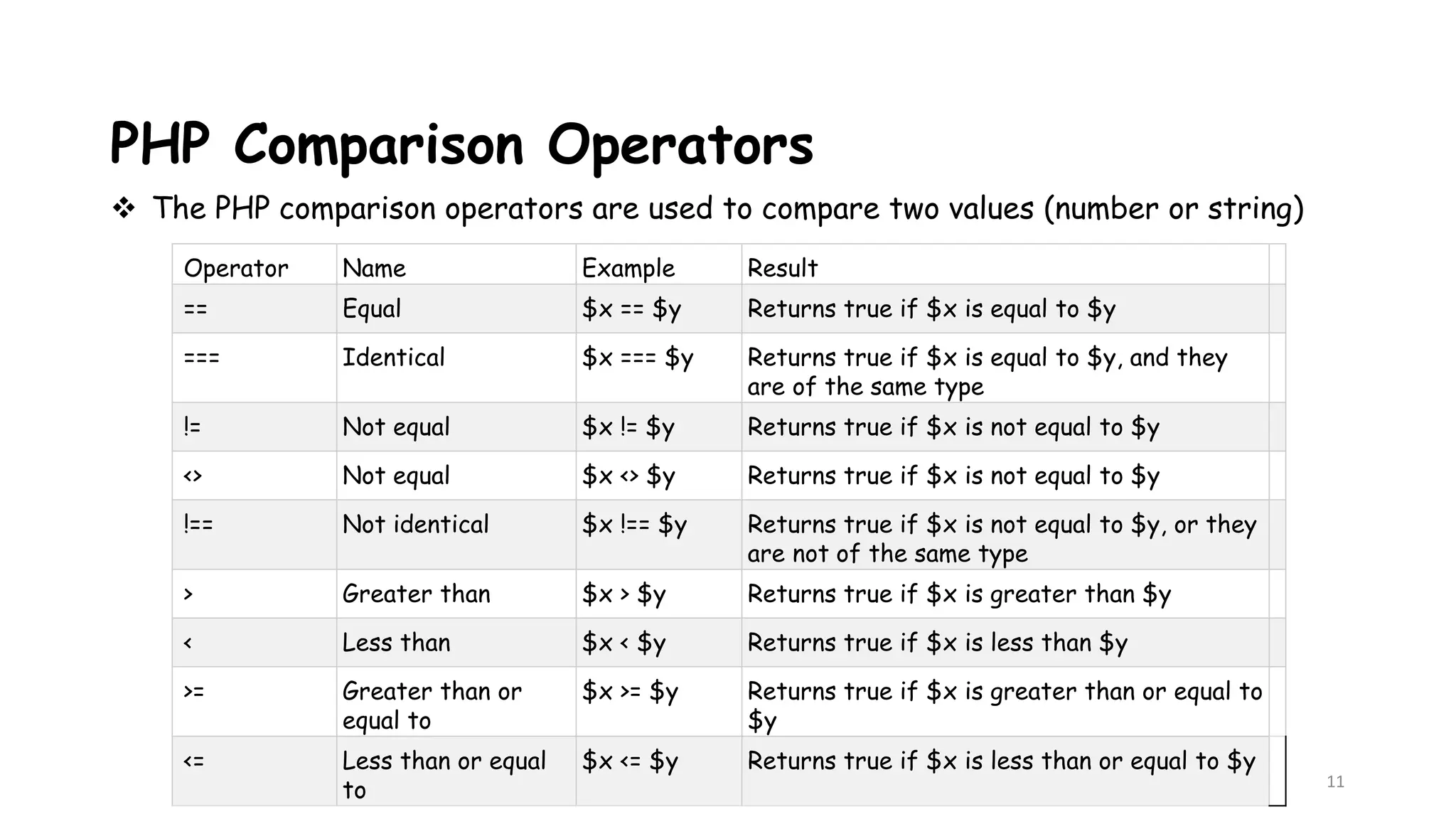
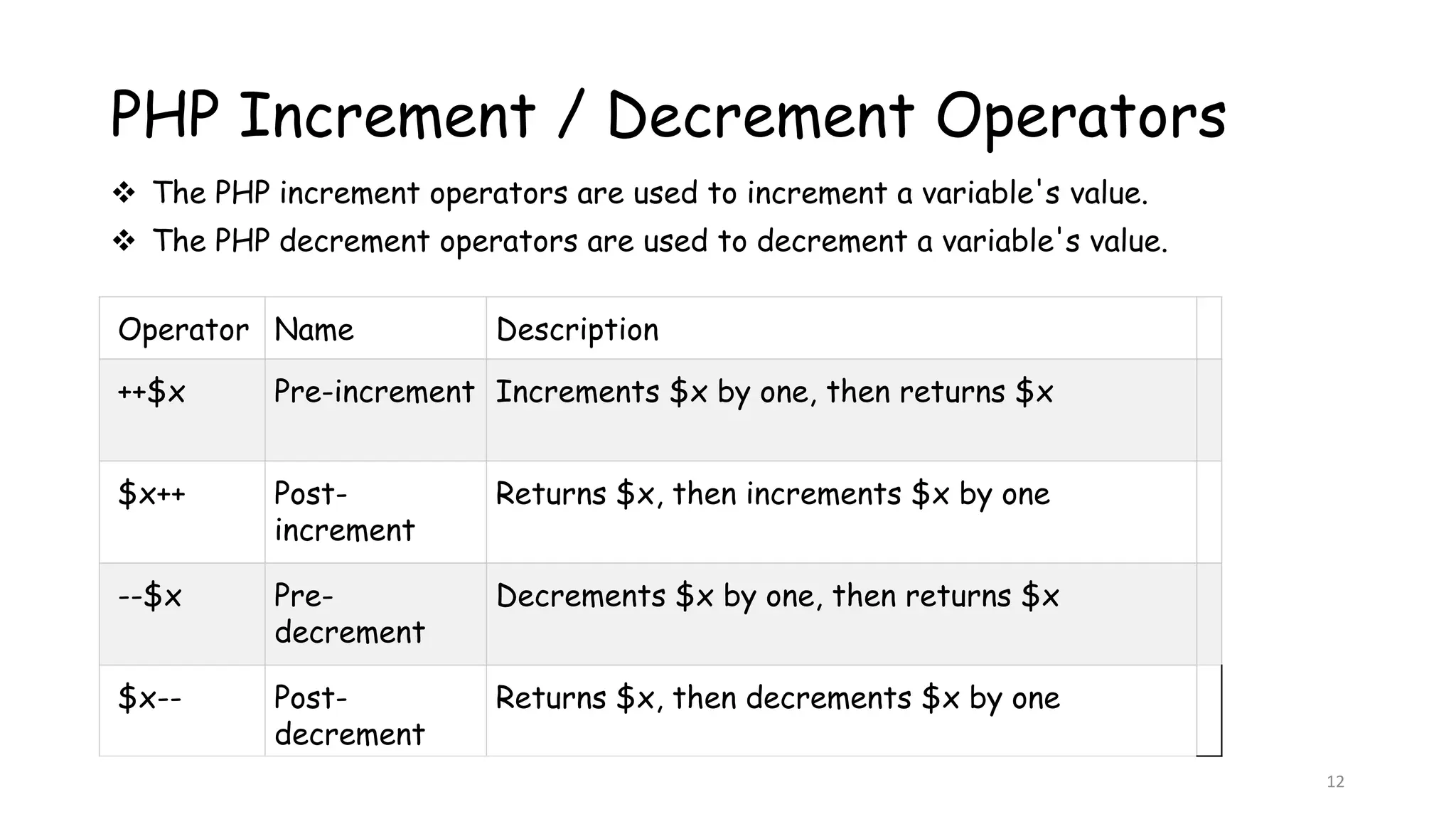
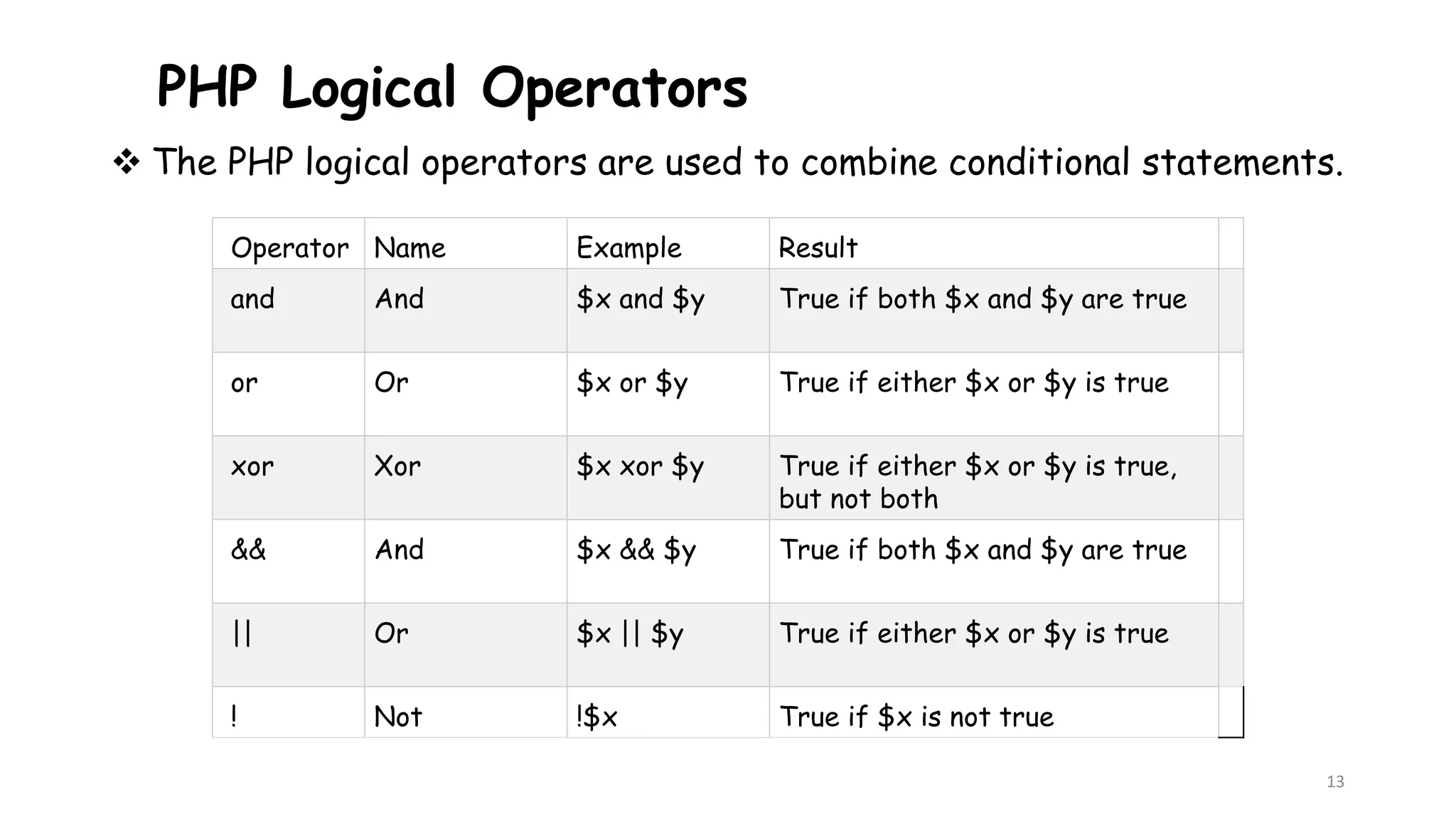
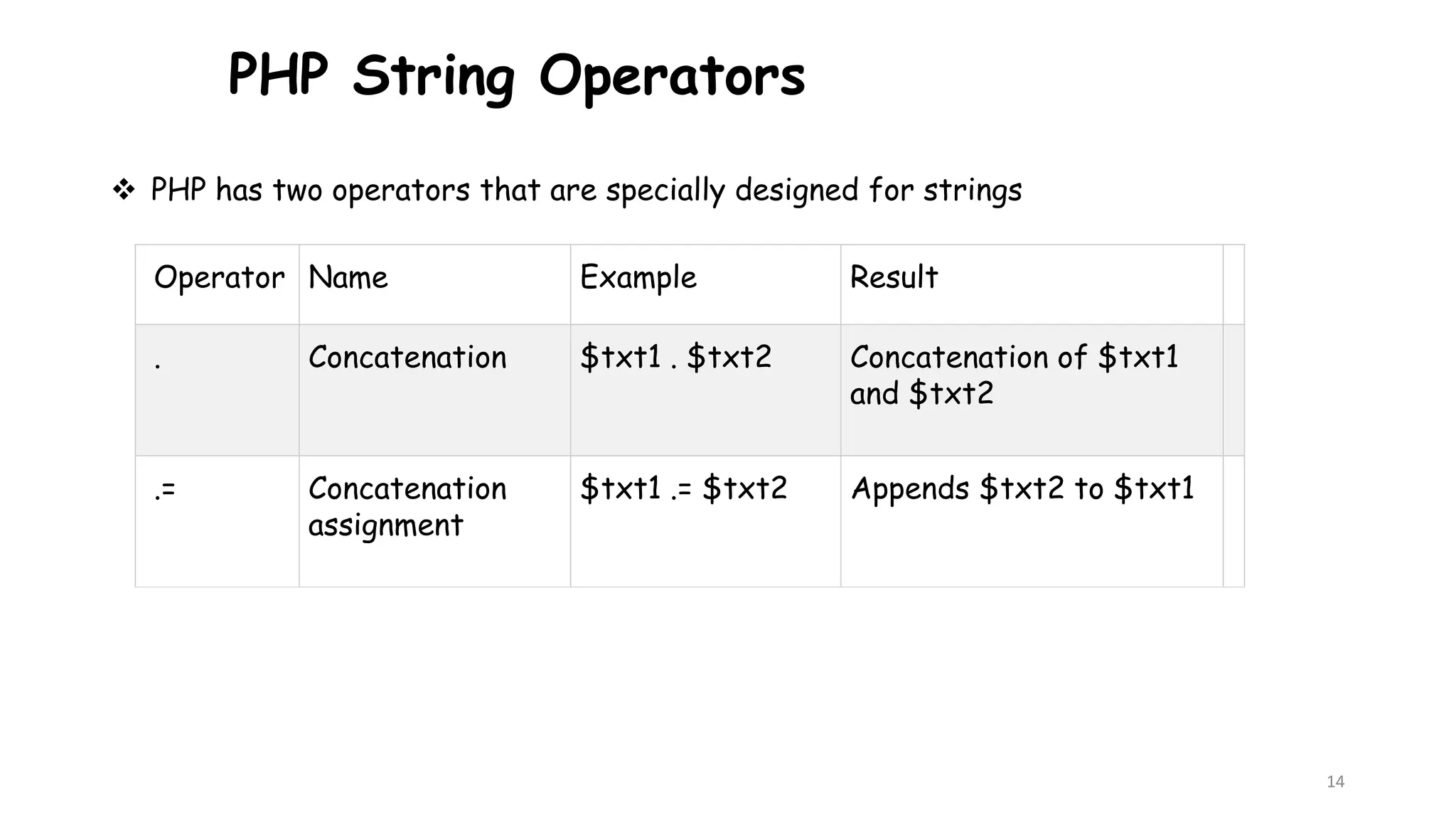
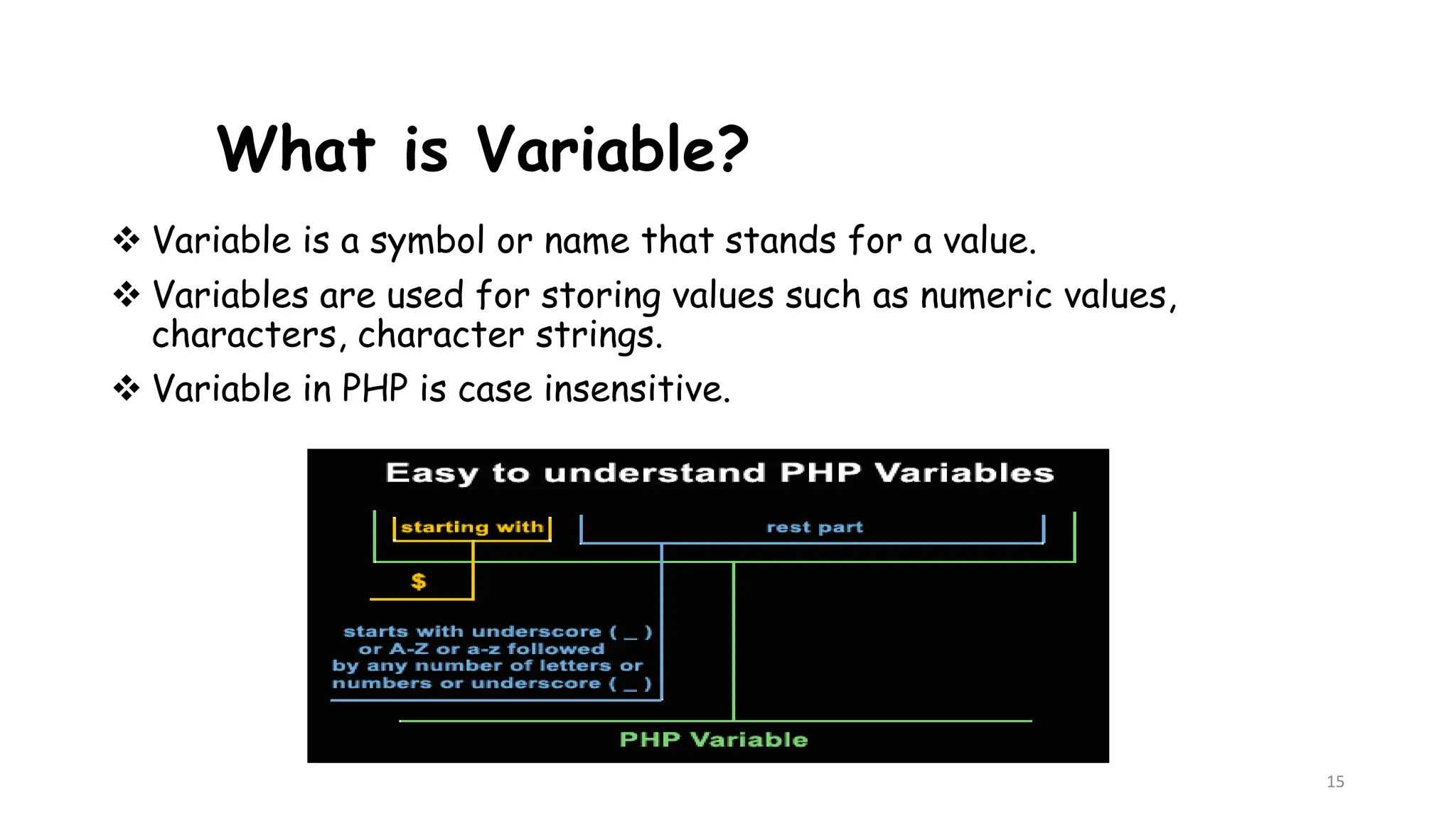
This document provides an introduction to PHP, describing its history, basic syntax, and programming operations. It explains PHP as a high-level, server-side scripting language used for web development and database management. The document also presents various operators, including arithmetic, assignment, comparison, increment/decrement, logical, and string operators, along with their functionalities.