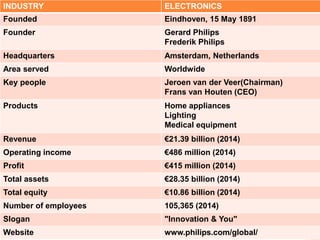
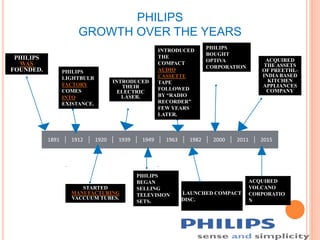
Royal Philips Electronics is a Dutch multinational conglomerate founded in 1891. Headquartered in Amsterdam, Philips has diversified operations in healthcare, lighting, and consumer electronics. In 2014, Philips reported revenues of €21.39 billion from its 105,365 employees across more than 60 countries. Philips has undergone restructuring initiatives to address financial struggles and shift to a more technology-focused brand known for innovation in areas like lighting solutions, healthcare equipment, and male grooming products.