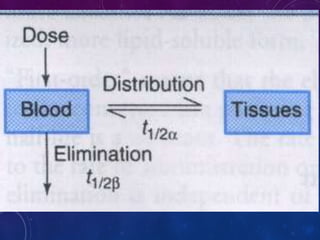
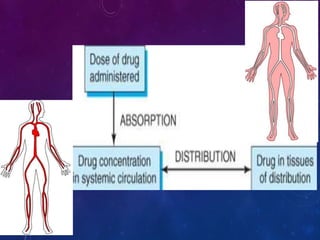
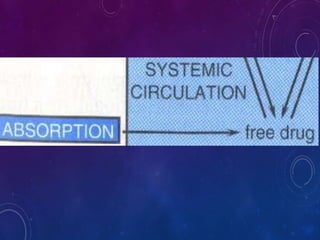
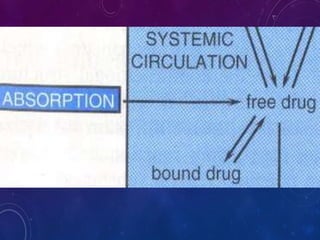
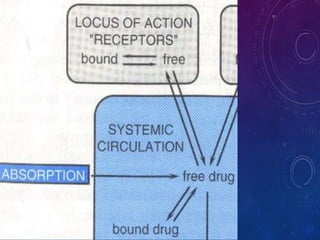
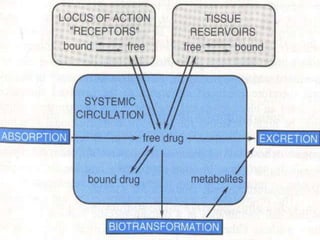
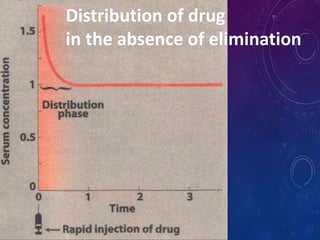
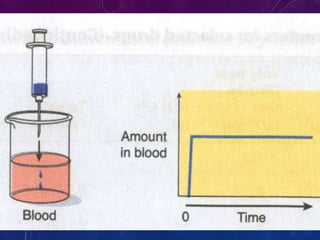
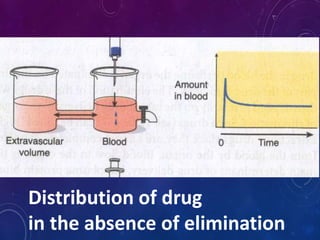
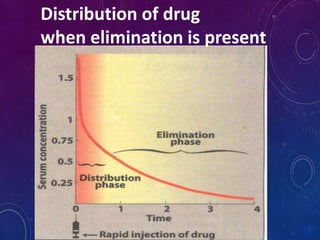
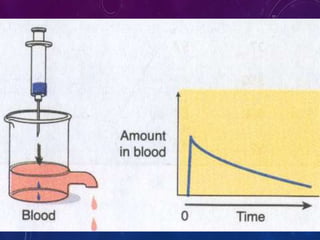
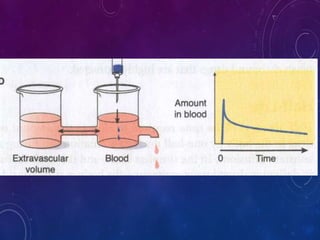
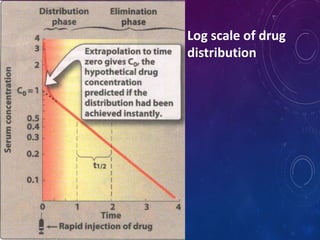
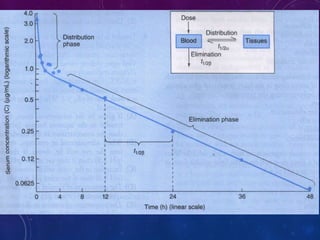
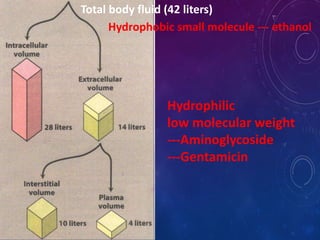
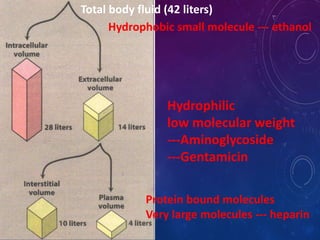
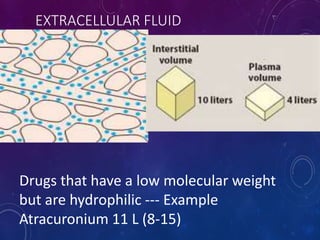
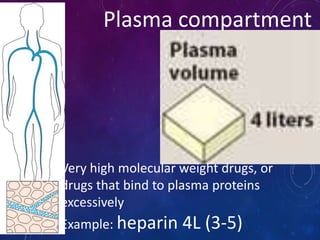
This document discusses the pharmacokinetics of drug distribution. It defines distribution as the movement of drugs from the bloodstream to tissues. Key points include:
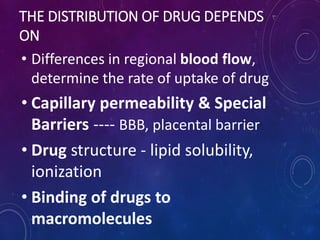
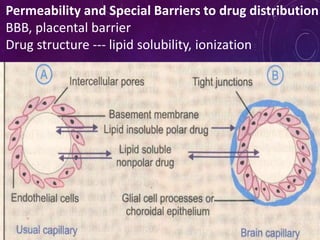
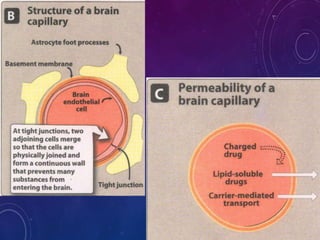
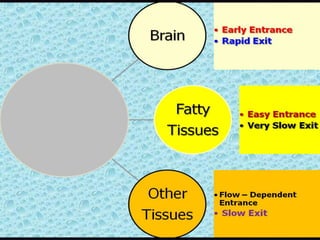
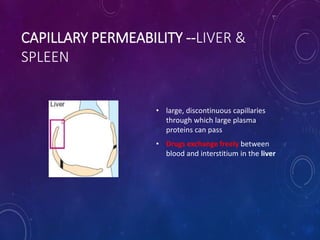
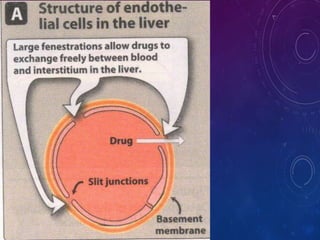
- Distribution depends on factors like regional blood flow, capillary permeability, and drug properties like lipid solubility and binding. Highly perfused organs like the brain, liver and kidneys show more initial distribution.
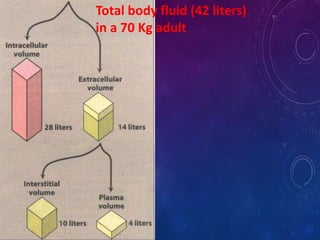
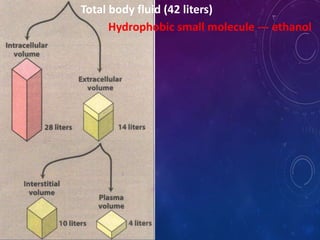
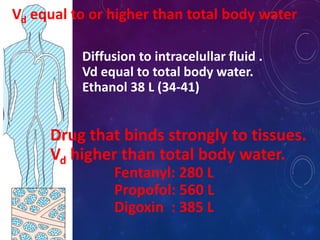
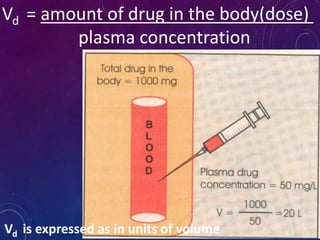
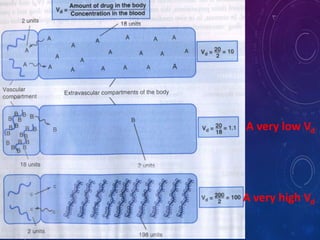
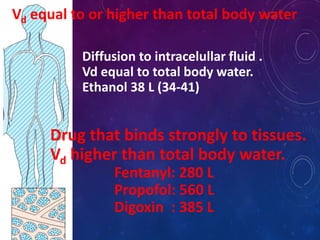
- The apparent volume of distribution (Vd) represents the volume needed to account for the amount of drug in the body based on plasma concentrations. A high Vd indicates extensive tissue binding while a low Vd may mean high plasma protein binding.
- Vd is used to calculate loading doses and amounts needed to achieve therapeutic concentrations. Disease