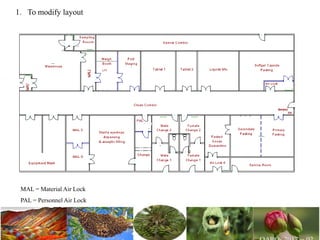
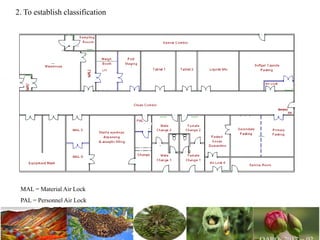
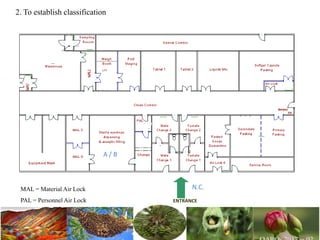
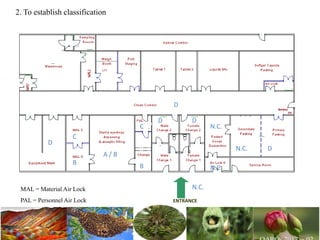
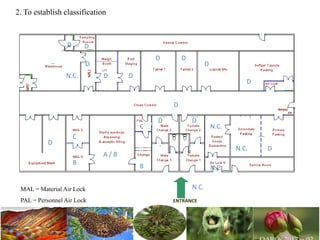
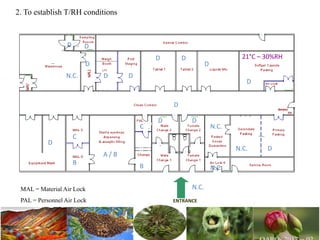
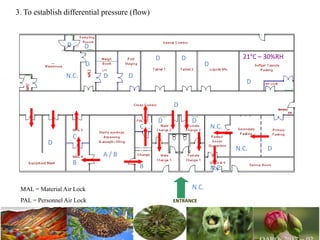
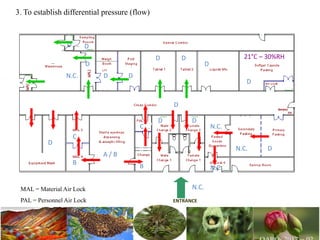
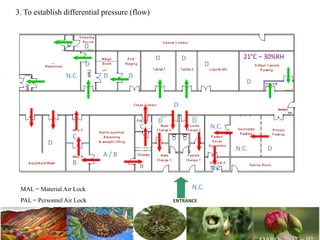
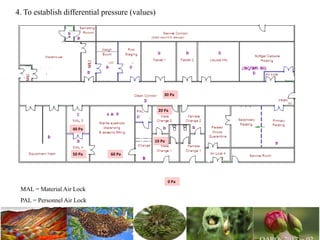
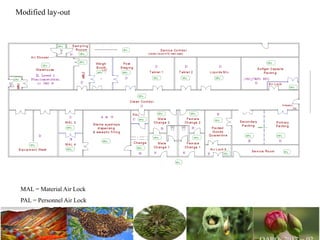
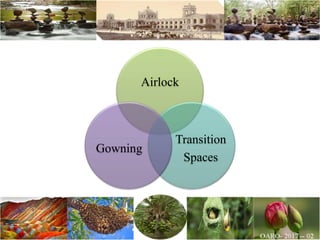
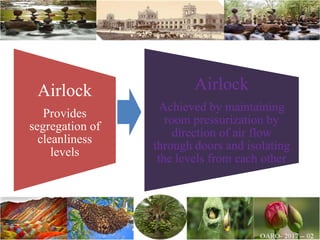
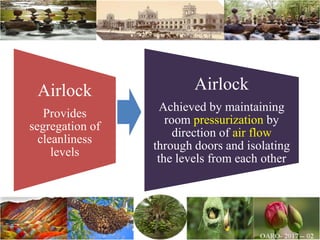
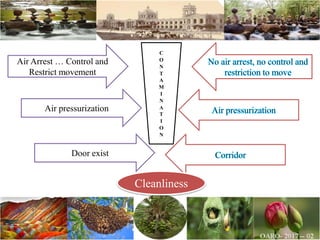
The document discusses the objectives and topics of a discussion forum on pharmaceutical engineering related to designing and maintenance of pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. The main objectives are to provide an interface among multidisciplinary teams to discuss science and regulations in a common language, and to provide an opportunity for knowledge sharing and transfer among pharmaceutical professionals from different educational backgrounds. The forum will also serve as a platform for engineers to exchange knowledge and learn about expanding regulatory expectations. The opening talk will be given by the Deputy Director of the Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan and will focus on regulatory experience and knowledge sharing without obligation on the regulatory agency. Some of the specific topics to be discussed include design principles in relation to GMP standards, importance of cleaning and maintenance, facility layout designs