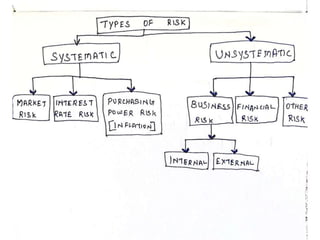
Portfolio management is a continuous process that involves identifying an investor's objectives, monitoring performance against targets, and adjusting to market conditions. Risk and return are closely related, as higher risk generally means higher potential returns. There are two main types of risk: systematic/market risk which stems from broader economic and political factors outside a company's control, and unsystematic/internal risk which is specific to a company such as business, financial, or social risks. Proper portfolio management aims to balance risks and returns according to an investor's preferences.