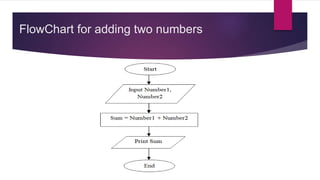
The document provides an overview of a programming fundamentals course, including assessment details, course goals, and an outline of topics to be covered. Some key topics include algorithms and pseudocode, flowcharts, types of programming languages including low-level languages like machine language and assembly language, and an introduction to problem solving and programming concepts. Assessment is based on midterm, final exams, assignments, quizzes and a presentation project.