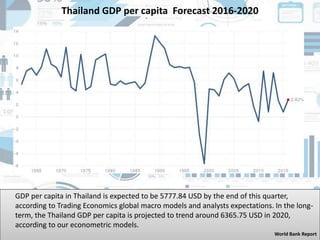
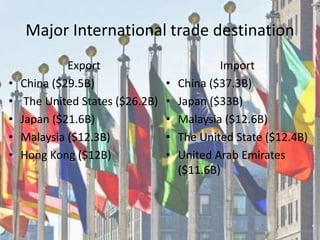
Thailand is a constitutional monarchy headed by King Rama X. The economy relies heavily on international trade, with key exports including vehicles, electronics, and rubber. The population is diverse and predominantly Buddhist. Traditional Thai culture is expressed through dances, martial arts like Muay Thai, and cuisine such as tom yum soup. The government promotes science and technology research to support economic growth while addressing environmental challenges like pollution and climate change impacts.