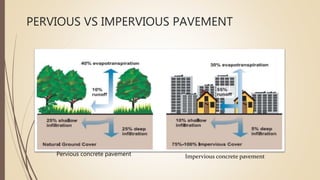
Pervious concrete is a high-porosity concrete used for various applications such as parking areas and walkways, allowing water infiltration to mitigate issues caused by stormwater on impervious surfaces. While it has advantages like groundwater recharge and reduced surface temperatures, challenges include high costs, longer curing times, and maintenance needs. Recent interest in pervious concrete has arisen due to environmental concerns and urban water management issues.