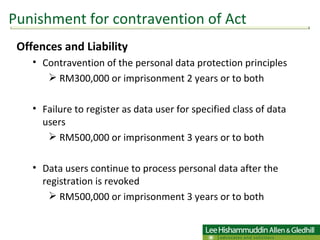
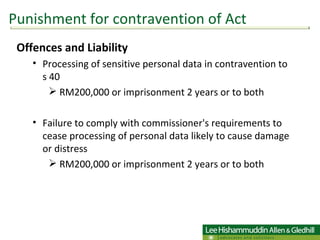
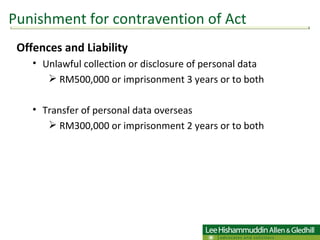
The document summarizes Malaysia's Personal Data Protection Act of 2010, which regulates the processing of personal data related to commercial transactions. It defines key terms, outlines 7 data protection principles, and discusses the rights of data subjects, offenses/penalties, and requirements for data users and sensitive personal data. It proposes a two-stage action plan for organizations to comply with the new law.
![Data Protection in Malaysia by Foong Cheng Leong [email_address] | [email_address] www.foongchengleong.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataprotectioninmalaysiafcljune2011-110704023940-phpapp01/75/Personal-Data-Protection-in-Malaysia-1-2048.jpg)
![Personal Data Protection Act 2010 [ Act 709 ] Gazetted: 10 June 2010 (not yet in force) Highlights of the Act](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataprotectioninmalaysiafcljune2011-110704023940-phpapp01/85/Personal-Data-Protection-in-Malaysia-2-320.jpg)