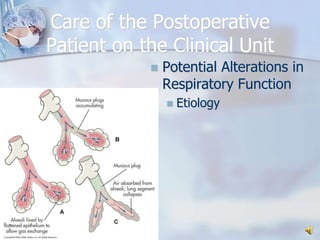
This document outlines preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative nursing care for surgical patients. It discusses the nursing assessment process including health history, physical exam, and psychosocial evaluation. Key parts of the nursing management are preoperative teaching, informed consent, preparing patients for surgery, and providing care in the operating room, PACU, and postoperative units. Potential postoperative complications are reviewed for multiple body systems along with the corresponding nursing care.