This document summarizes key concepts about the periodic table including:
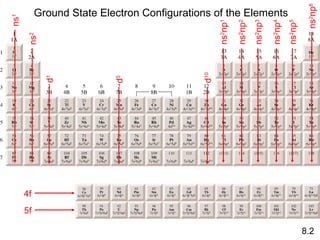
- How the elements were discovered and their electron configurations
- How cations and anions are formed by gaining or losing electrons to achieve a noble gas configuration
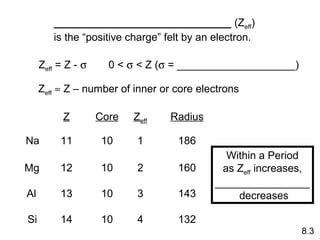
- Trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity across periods and down groups
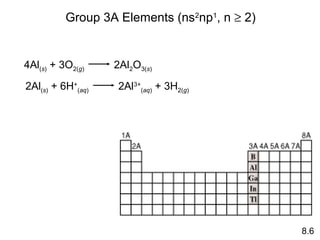
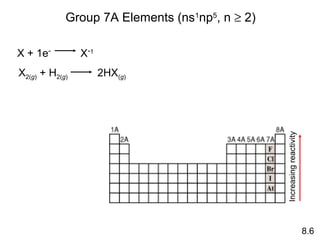
- How the reactivity of elements in groups 1A, 2A, 3A and 7A changes based on their tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons.



![Electron Configurations of Cations and Anions
Na [Ne]3s1
Na+
[Ne]
Ca [Ar]4s2
Ca2+
[Ar]
Al [Ne]3s2
3p1
Al3+
[Ne]
Atoms ___________ electrons
so that cation has a noble-gas
outer electron configuration.
H 1s1
H-
1s2
or [He]
F 1s2
2s2
2p5
F-
1s2
2s2
2p6
or [Ne]
O 1s2
2s2
2p4
O2-
1s2
2s2
2p6
or [Ne]
N 1s2
2s2
2p3
N3-
1s2
2s2
2p6
or [Ne]
Atoms ____________
electrons so that anion
has a noble-gas outer
electron configuration.
Of Representative Elements
8.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodictable-131009101040-phpapp02/85/Periodic-table-5-320.jpg)

![Na+
: [Ne] Al3+
: [Ne] F-
: 1s2
2s2
2p6
or [Ne]
O2-
: 1s2
2s2
2p6
or [Ne] N3-
: 1s2
2s2
2p6
or [Ne]
Na+
, Al3+
, F-
, O2-
, and N3-
are all ________________ with Ne
What neutral atom is isoelectronic with H-
?
__________________________________
8.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodictable-131009101040-phpapp02/85/Periodic-table-7-320.jpg)
![Electron Configurations of Cations of Transition Metals
8.2
When a ___________________ is formed from an atom of a
_______________________, electrons are always removed
first from the ns orbital and then from the (n – 1)d orbitals.
Fe: [Ar]4s2
3d6
Fe2+
: [Ar]4s0
3d6
or [Ar]3d6
Fe3+
: [Ar]4s0
3d5
or [Ar]3d5
Mn: [Ar]4s2
3d5
Mn2+
: [Ar]4s0
3d5
or [Ar]3d5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodictable-131009101040-phpapp02/85/Periodic-table-8-320.jpg)