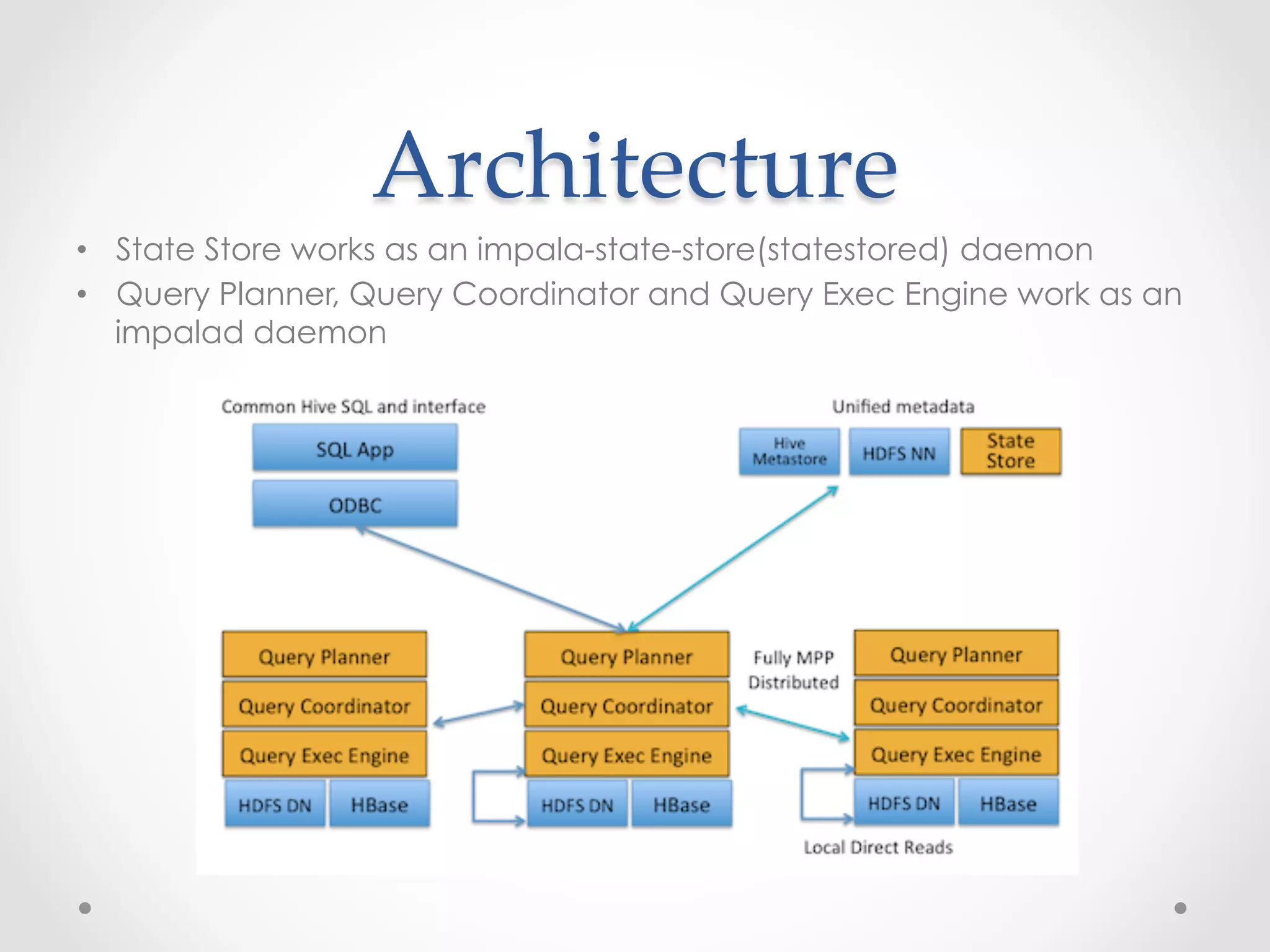
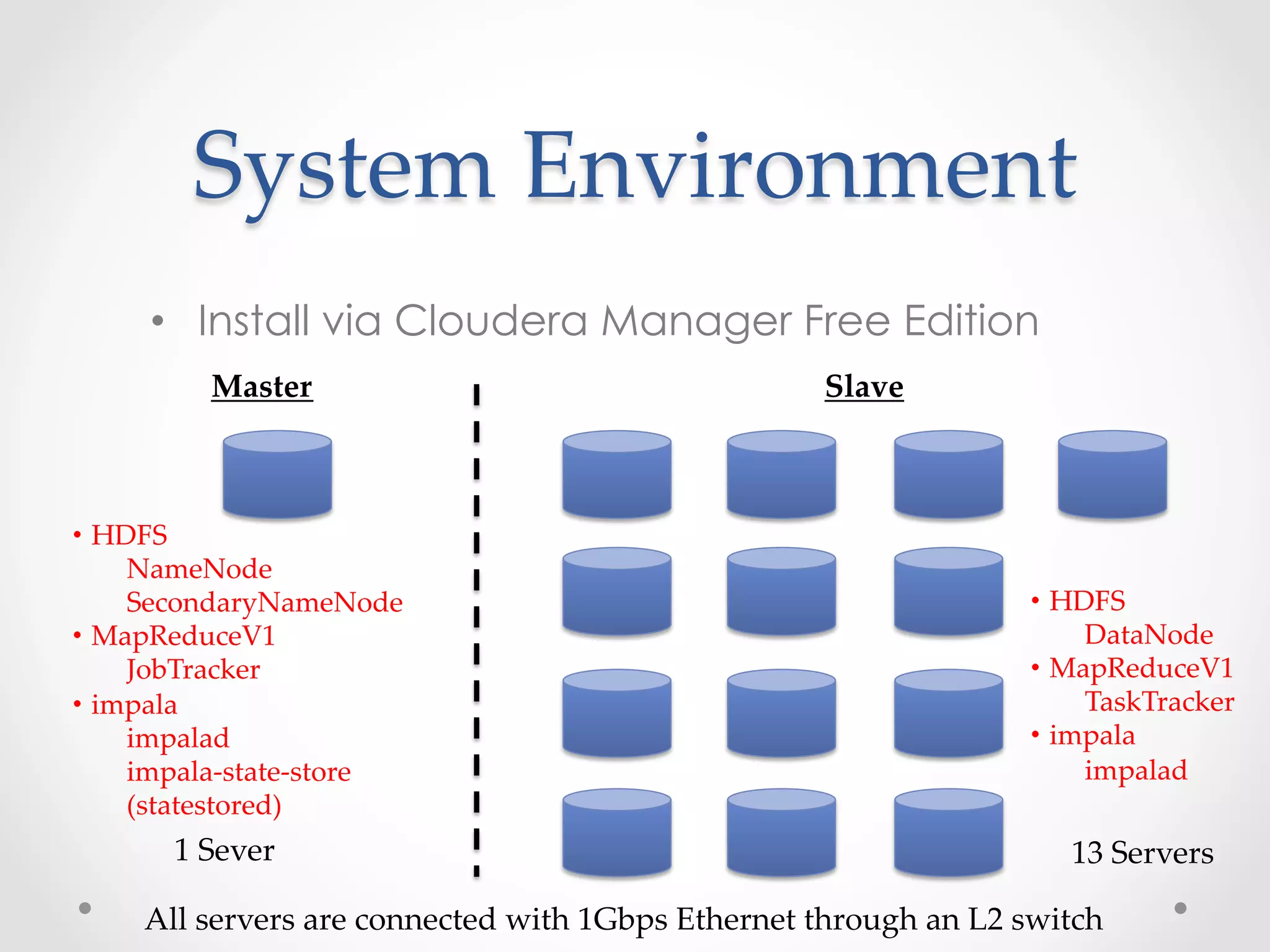
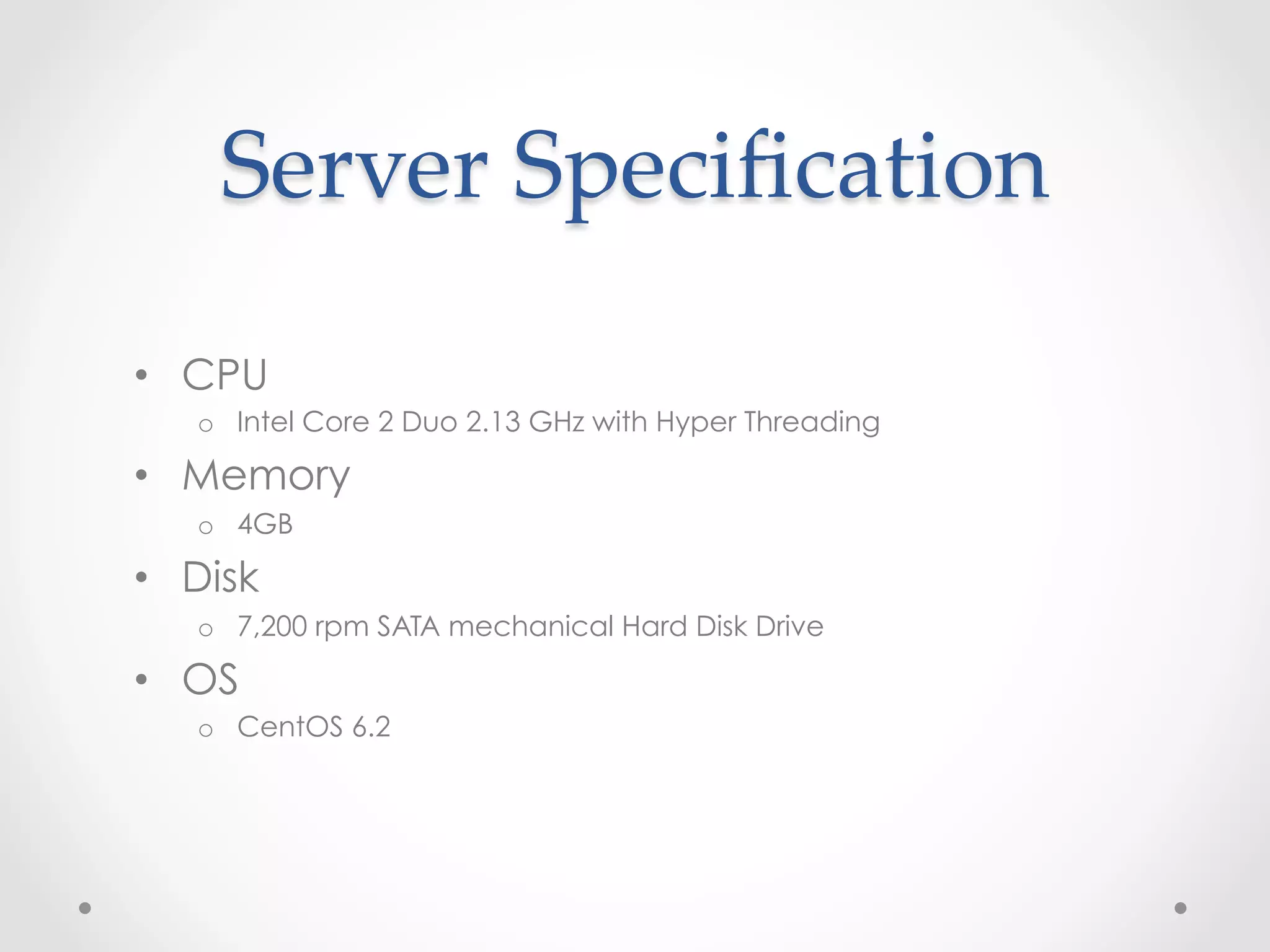
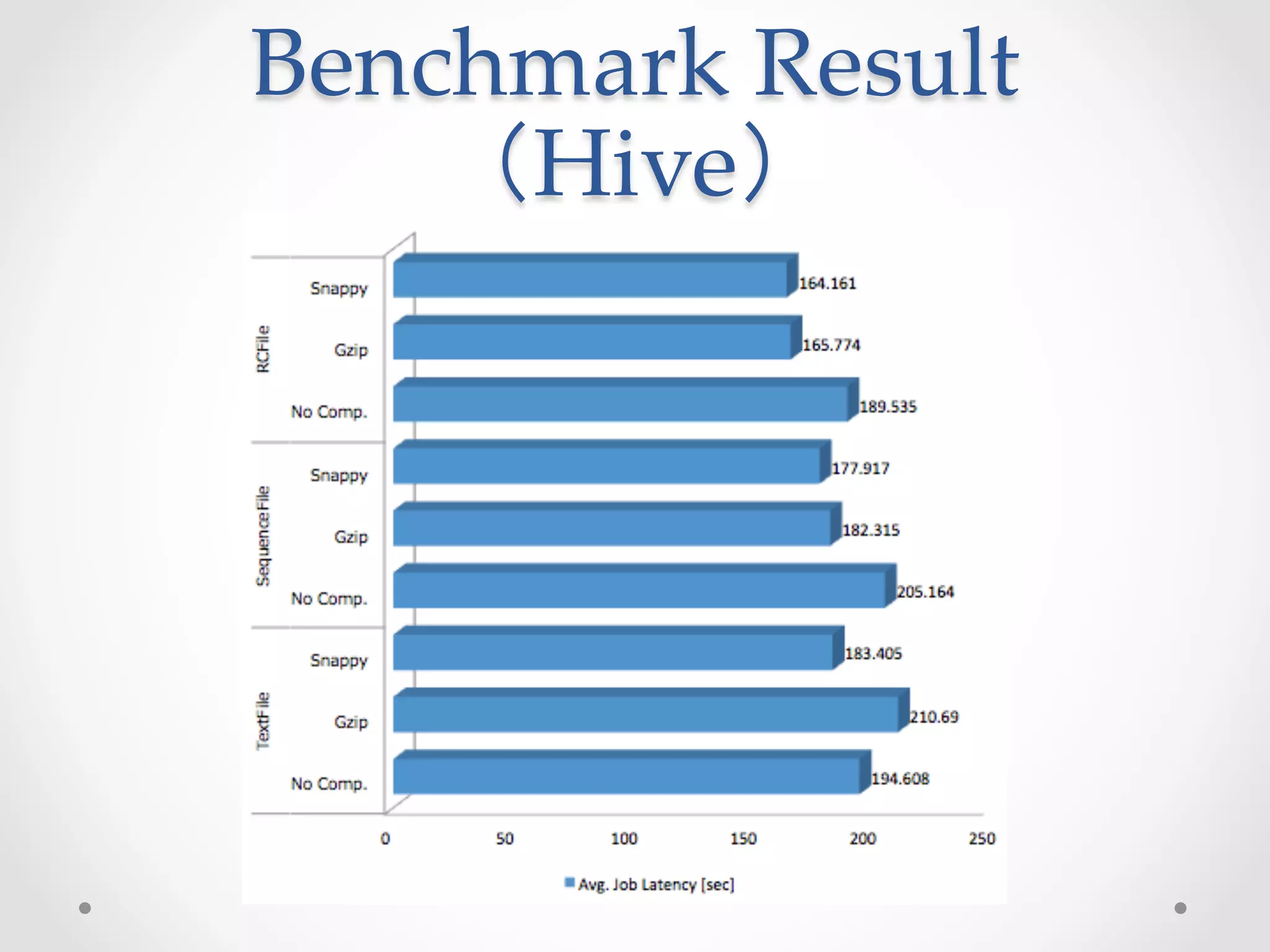
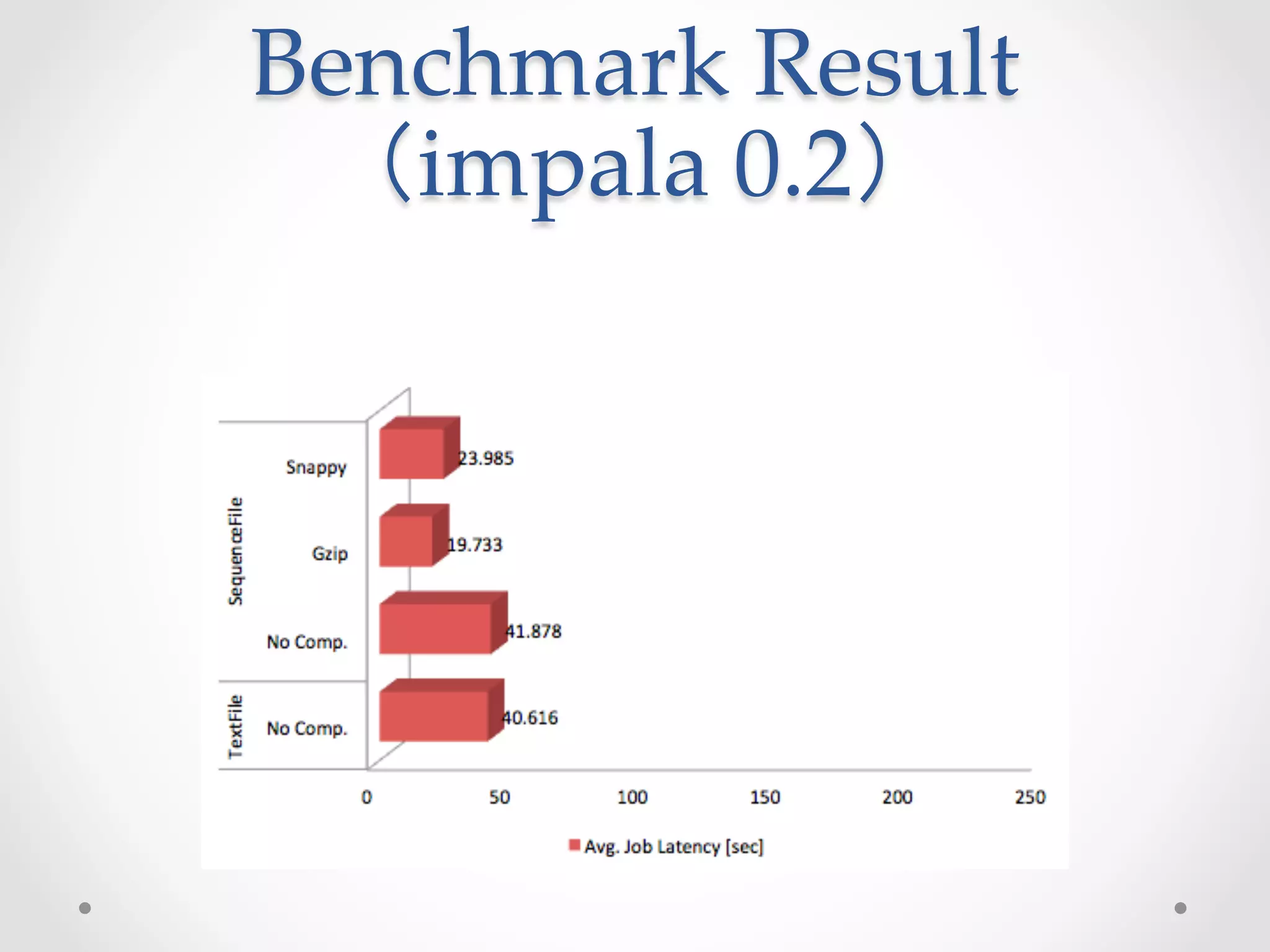
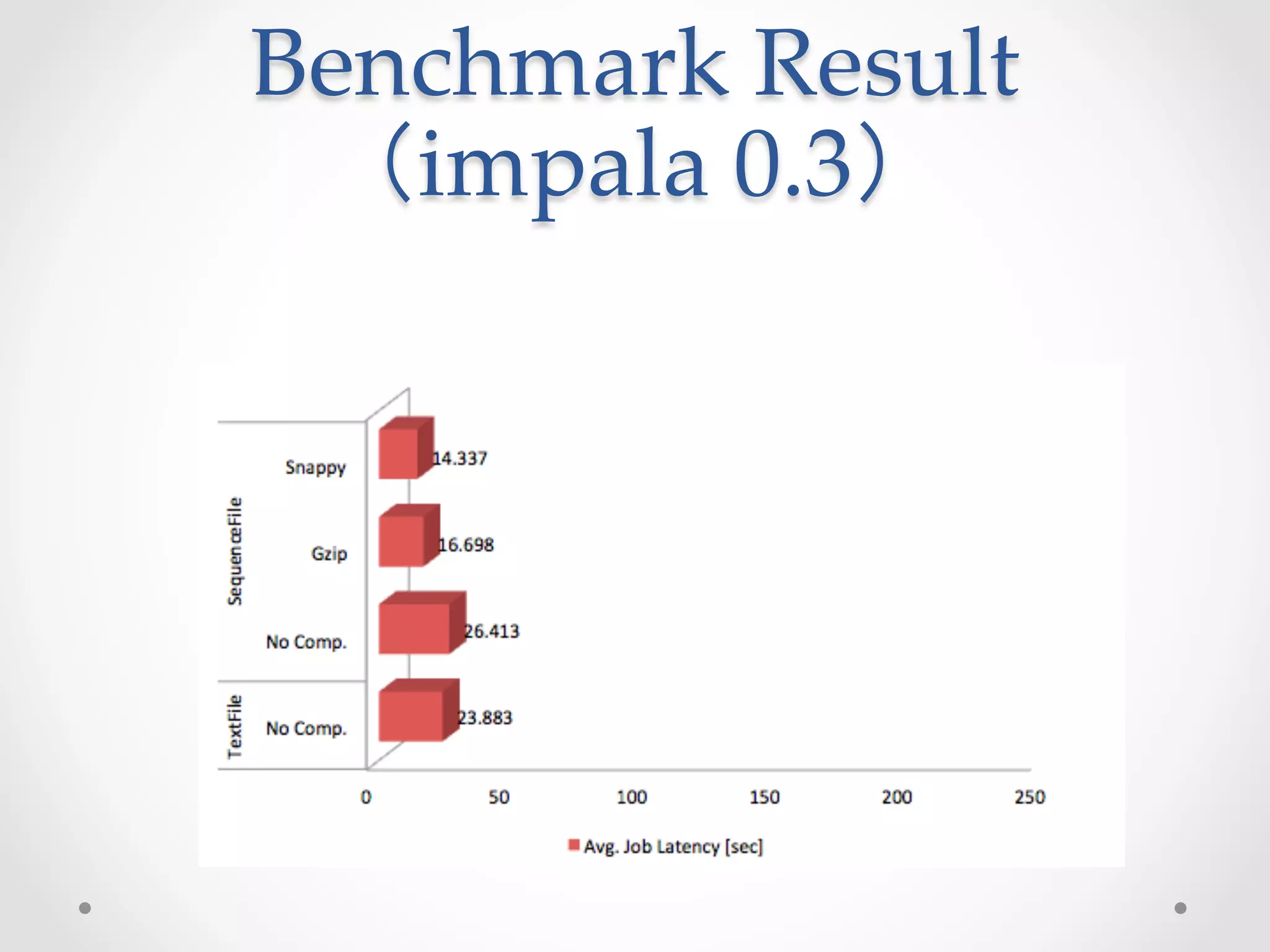
This document evaluates the performance of Cloudera Impala, an open-source SQL query engine for Apache Hadoop, and compares it to Apache Hive. It describes Impala's architecture and how the benchmark was conducted. The benchmark found Impala to be over 10 times faster than Hive for the modified TPC-H query, with the fastest Impala version taking 14.337 seconds compared to 164.161 seconds for Hive. The document concludes that future versions of Impala integrated with CDH5 may provide even better performance by supporting additional file formats.