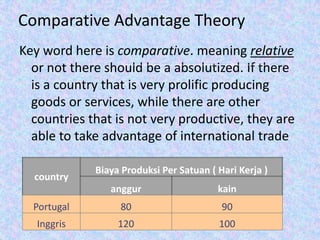
This document discusses international trade and globalization. It defines international trade as trade between residents of one country with other countries based on mutual agreement. Factors that encourage international trade include meeting domestic goods/service needs, increasing state revenues, market expansion, and technology transfer. Benefits are obtaining goods not produced domestically and gains from specialization. Theories discussed include absolute advantage theory and comparative advantage theory. Globalization is defined as the process of international integration arising from cultural interchange. Characteristics are constant change, interdependent production across countries, and increased cultural interaction through mass media. Benefits of globalization include increased global production and prosperity, while risks include inhibiting industrial growth and financial sector instability.