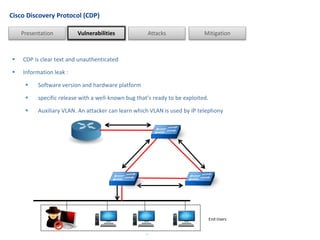
Layer 2 protocols like CDP, VTP, DTP, and HSRP are vulnerable to attacks if not properly secured. An attacker can use tools like Yersinia to perform reconnaissance on layer 2 protocols to gain information about devices, protocols, and network topology. Common attacks include denial of service attacks, traffic hijacking, and bypassing network restrictions. To prevent attacks, companies should secure switches, use secure trunking configurations, disable unused ports and protocols, and deploy security features like DHCP snooping.