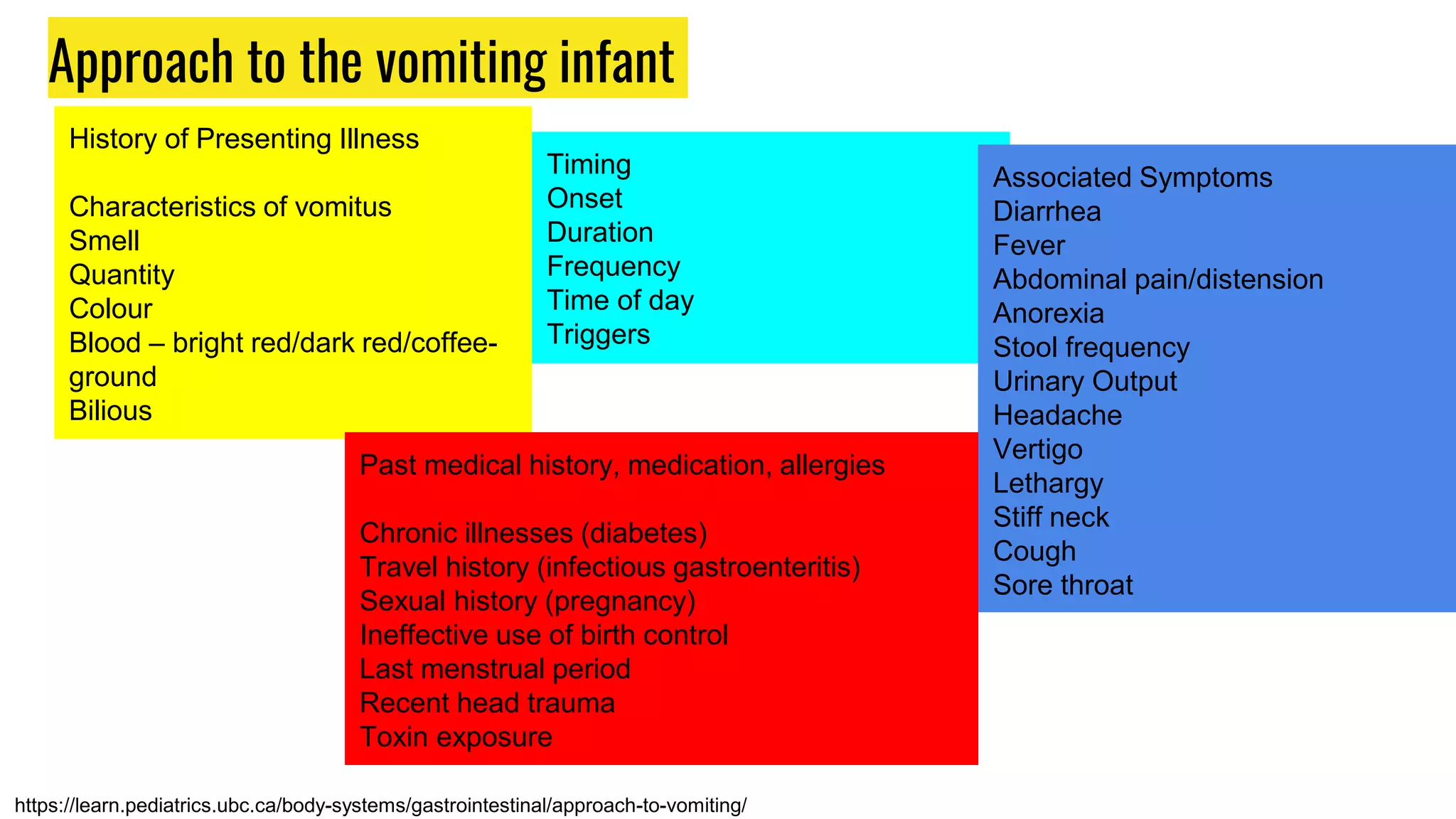
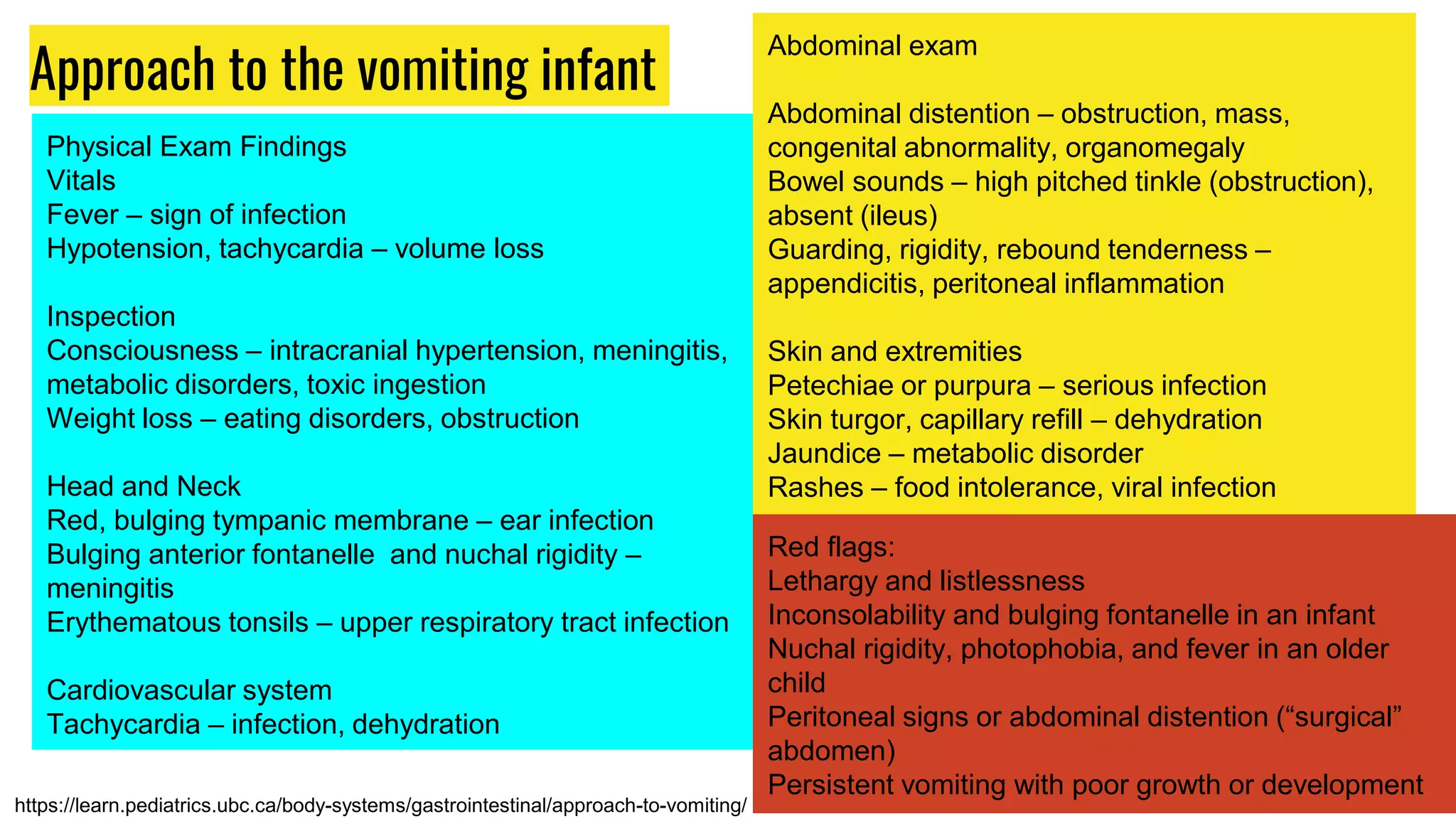
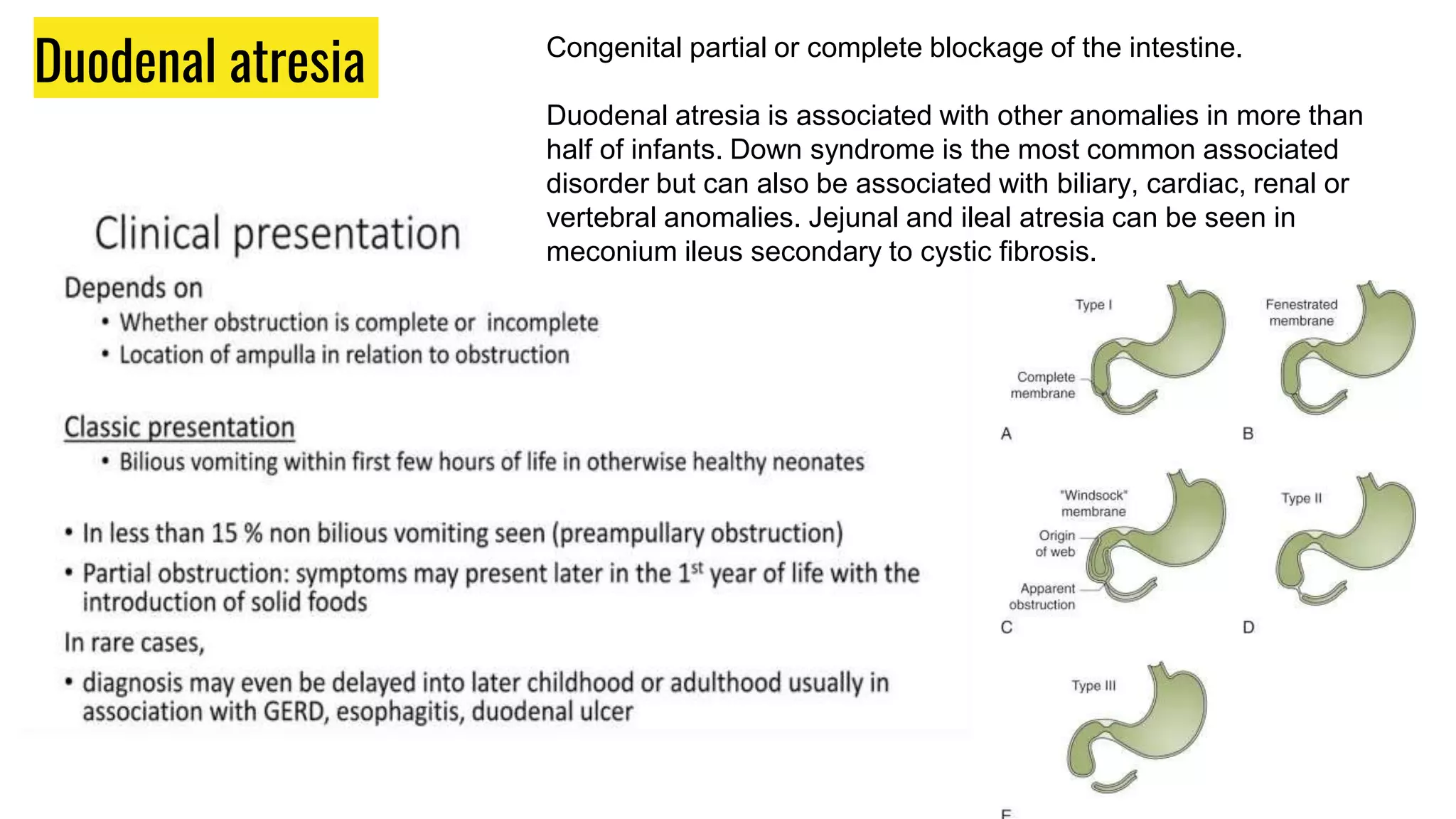
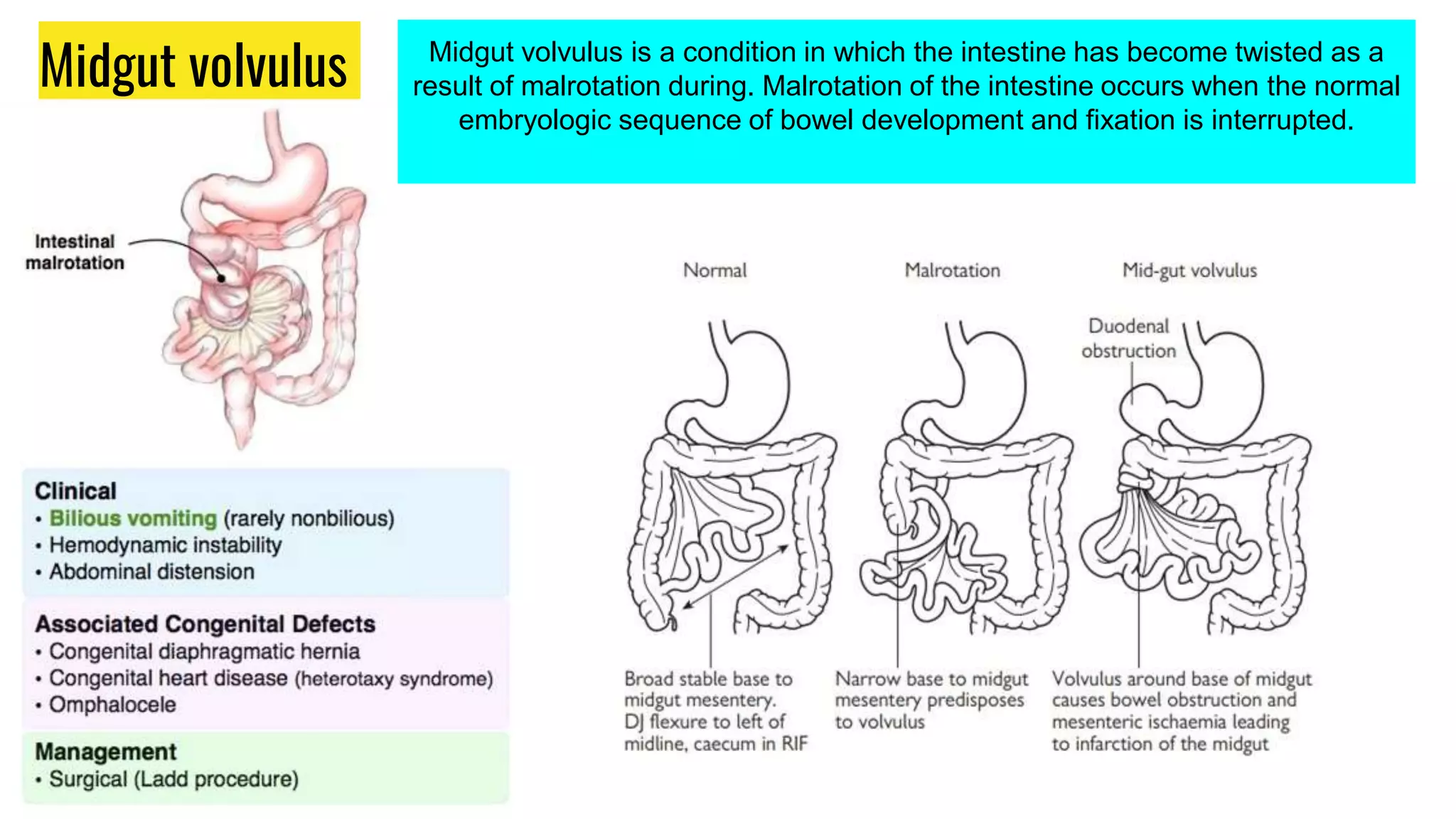
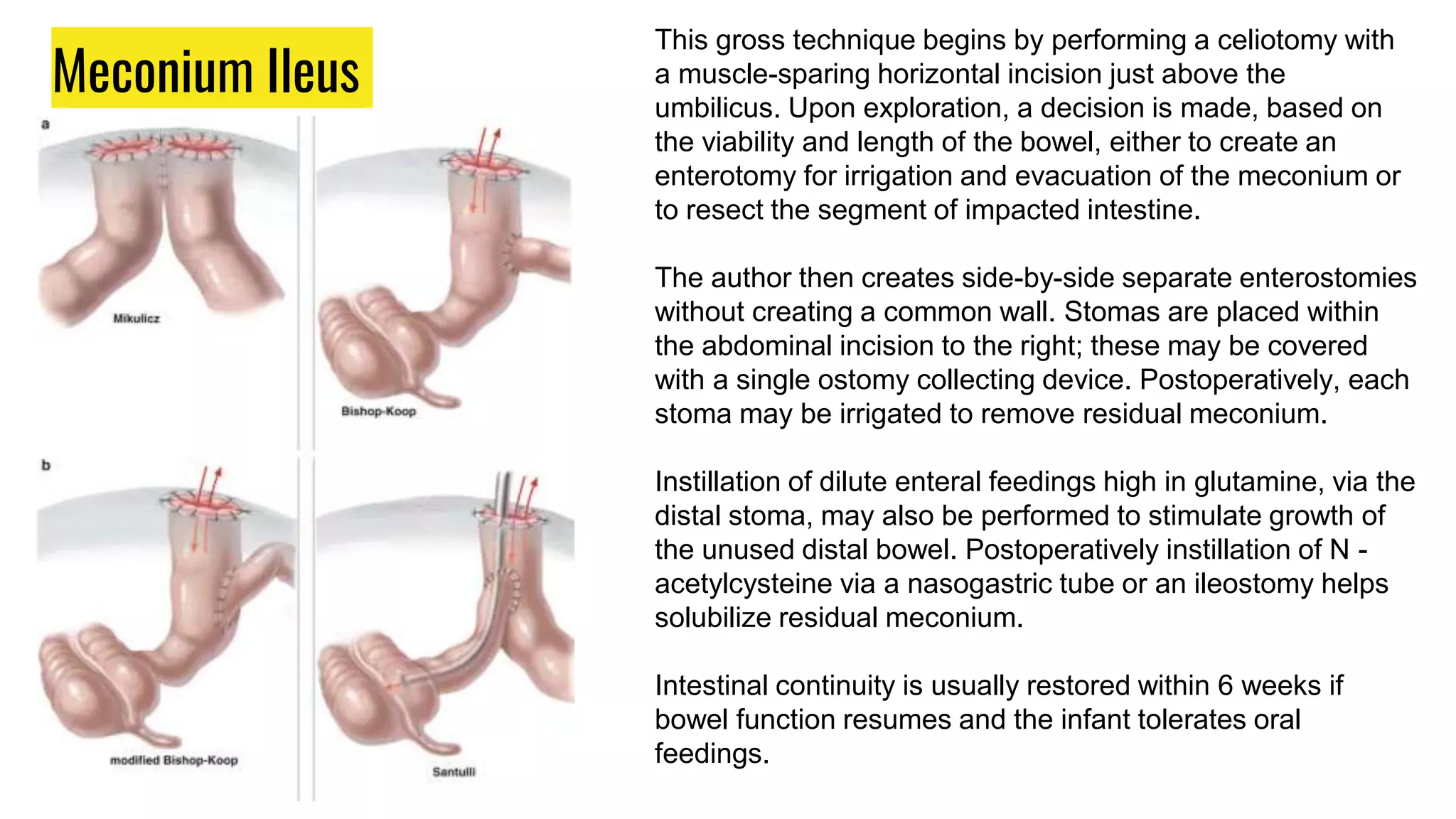
This document provides an overview of common gastrointestinal abnormalities seen in pediatric patients. It discusses conditions such as vomiting, hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, duodenal atresia, intestinal malrotation, midgut volvulus, meconium ileus, necrotizing enterocolitis, Meckel's diverticulum, intussusception, appendicitis, Hirschsprung disease, mesenteric cysts, and anorectal malformations. For each condition, it provides a brief definition and discussion of relevant physical exam findings, diagnostic approaches, and treatment considerations for pediatric patients.