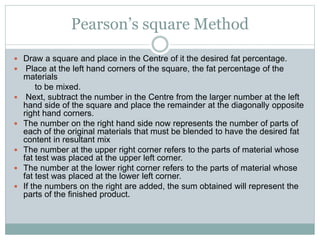
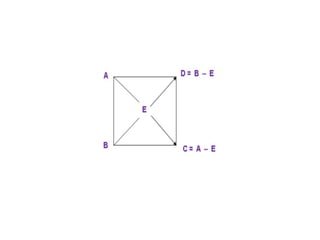
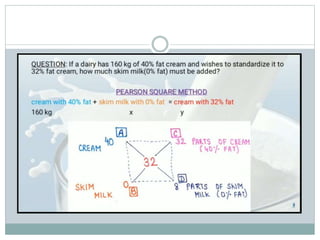
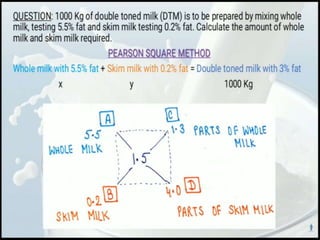
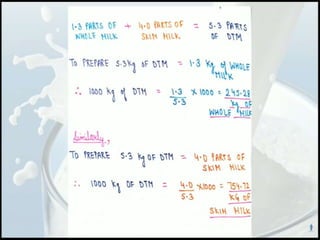
The document discusses the estimation of fat and SNF content in milk using Pearson's method, which involves adjusting milk constituents to meet legal requirements. It outlines the process of using Pearson's square to mix materials to achieve desired fat content, focusing on standardization practices in the milk industry. Limitations of the method include its applicability to only two ingredients and the requirement that the target fat percentage must fall between the values of the ingredients used.