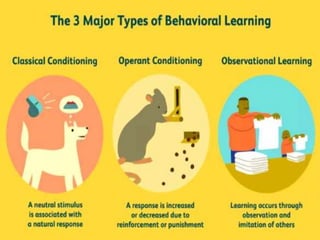
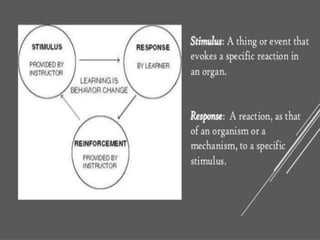
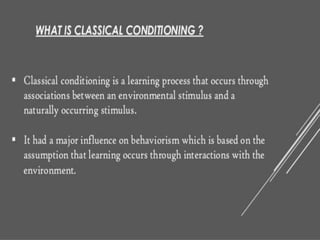
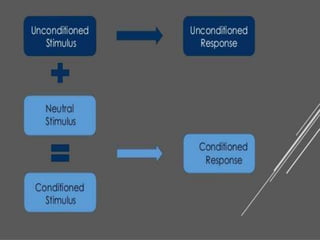
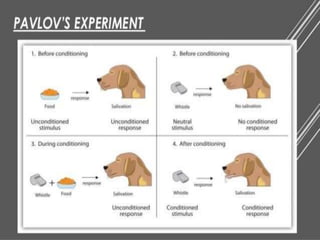
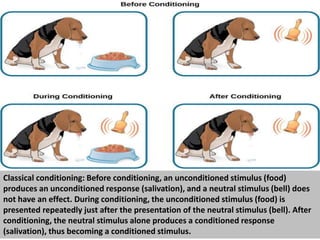
The document discusses learning and cognition. It defines learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience. It outlines several types of learning, including motor learning, verbal learning, concept learning, discrimination learning, learning principles, problem solving, and attitude learning. Classical conditioning is discussed, including Pavlov's experiment which demonstrated that a neutral stimulus can produce a conditioned response through repeated pairing with an unconditioned stimulus that naturally elicits a response. The four factors of classical conditioning are identified as the unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response.