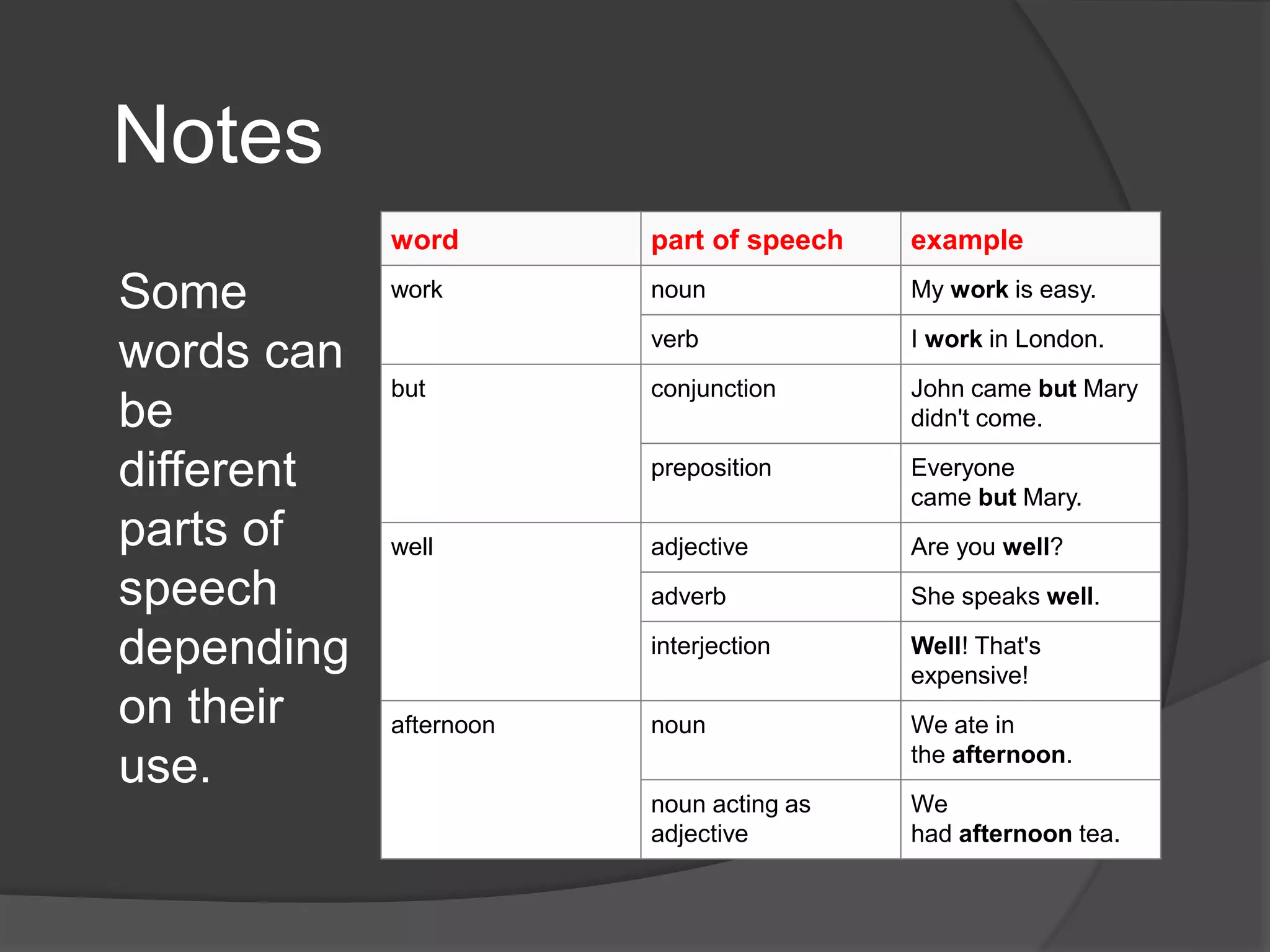
The document outlines the eight parts of speech in English: noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, and interjection, providing definitions and examples for each. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these parts for improving listening, reading, writing, and speaking skills. Additionally, the document explains how to construct sentences using various parts of speech and illustrates the flexibility of certain words depending on their use.