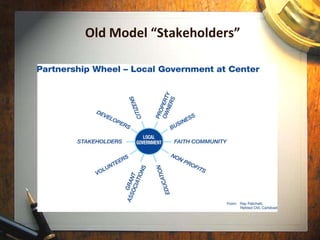
The document discusses the challenges of partnering between local governments and communities, highlighting a pervasive mistrust and a divide where the public acts as consumers rather than engaged citizens. It emphasizes the need for a shift in attitudes from both parties, advocating for community involvement through civic engagement and collaboration. The historical context shows that stronger community bonds can lead to improved social outcomes across various areas, necessitating a mutual effort to foster partnerships for effective problem-solving.