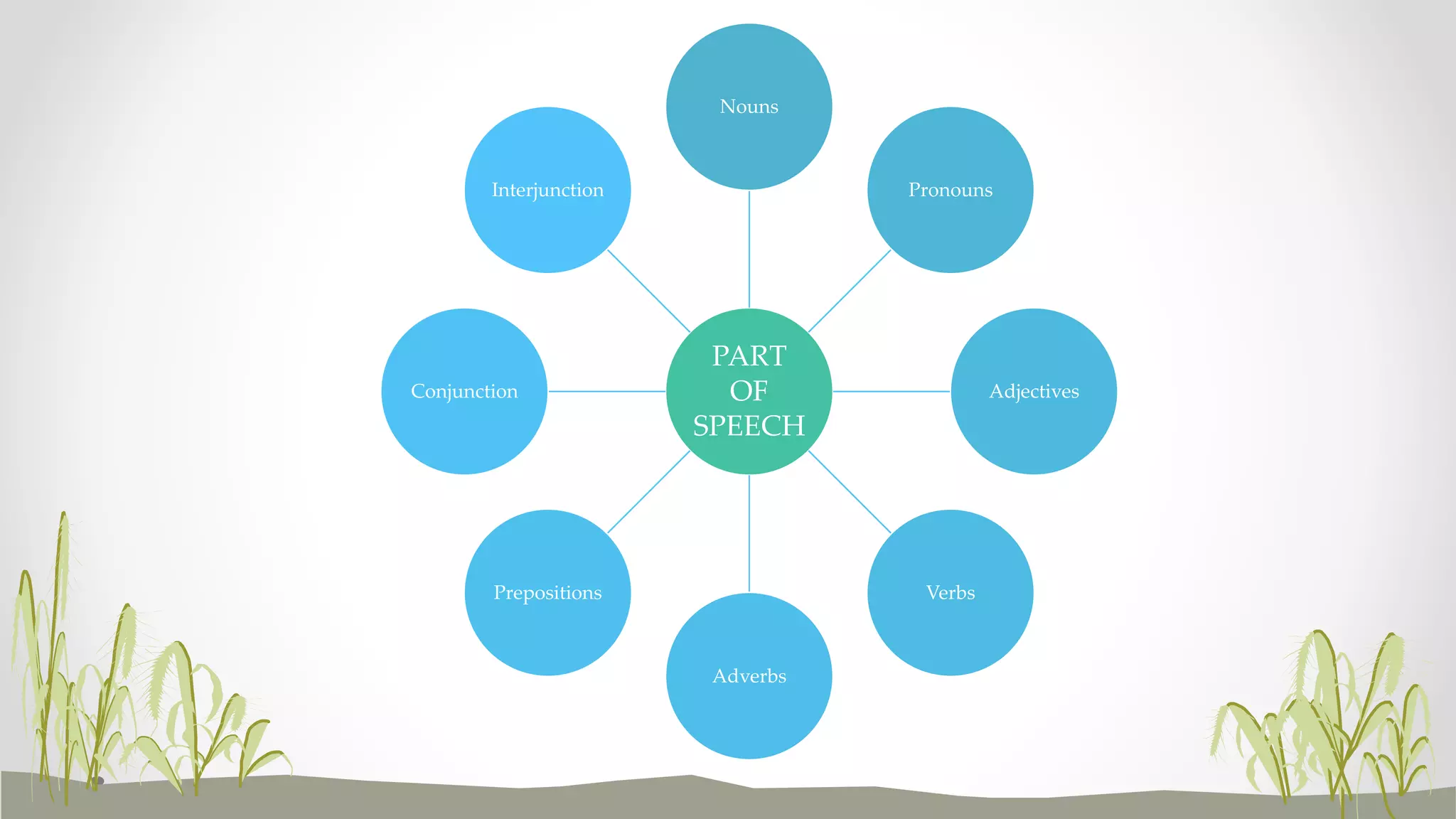
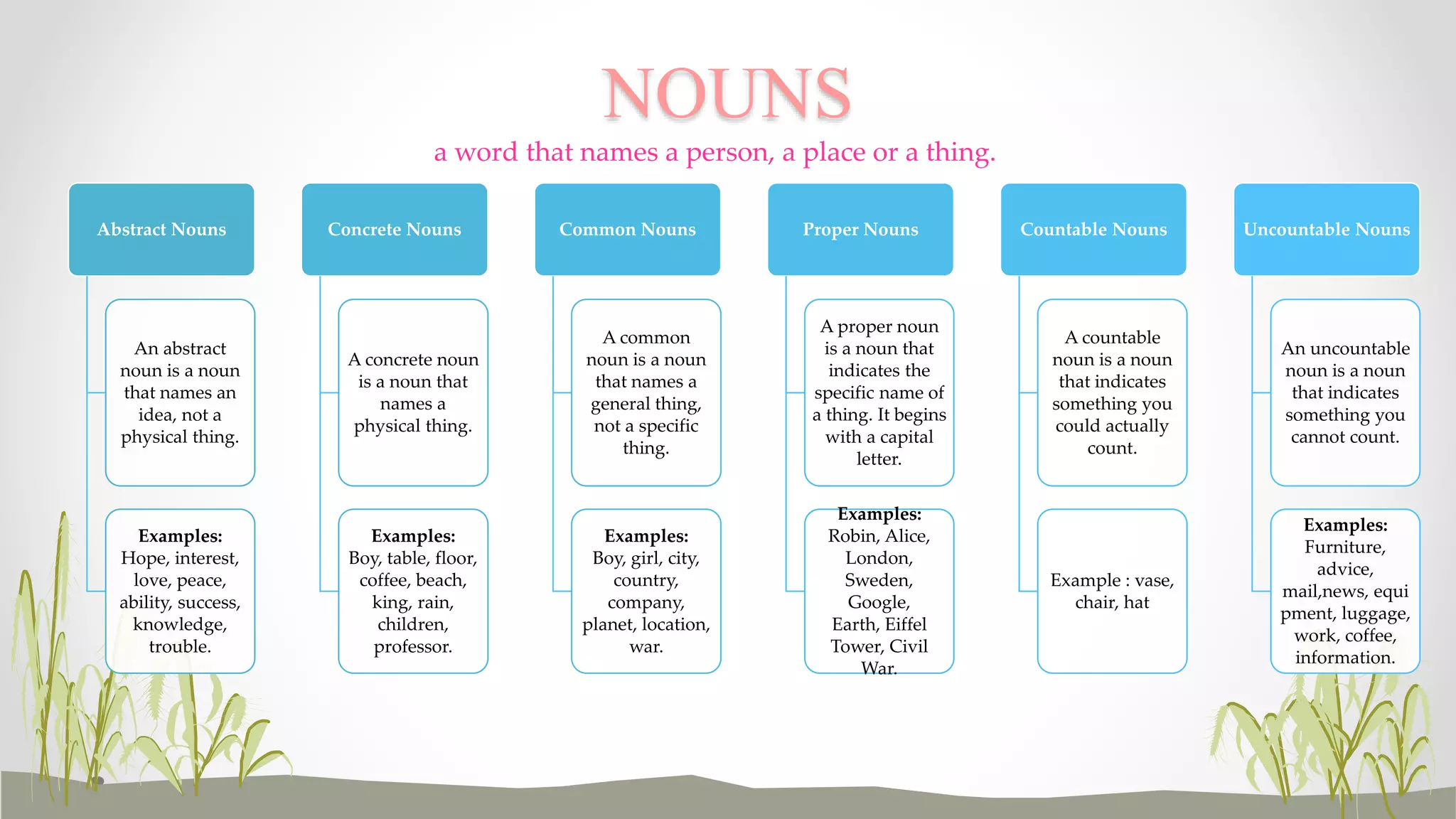
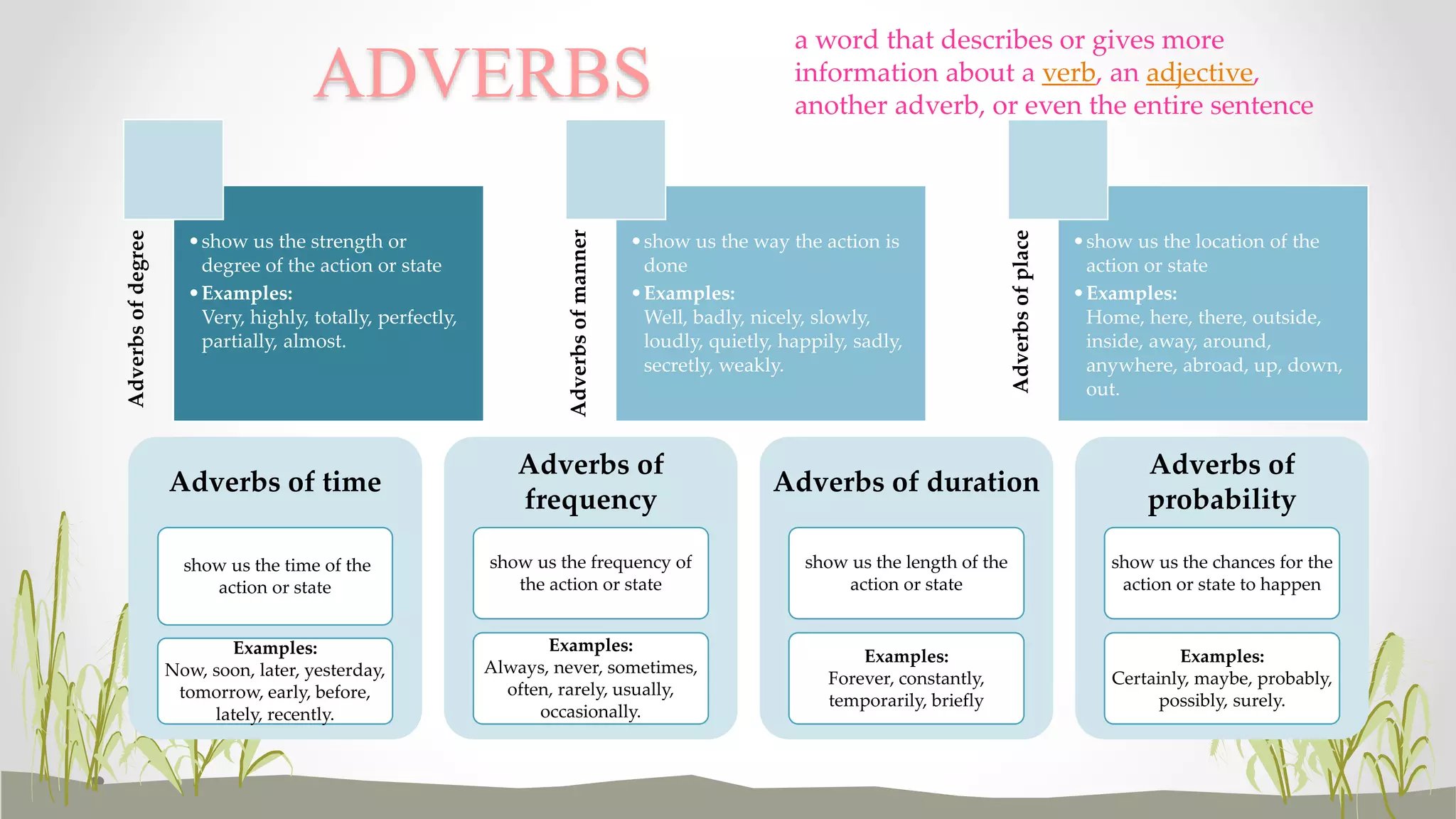
This document provides definitions and examples of the different parts of speech in English including nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. For each part of speech, it lists the types and provides short descriptive definitions. It also includes exercises for readers to practice identifying examples of each part of speech.