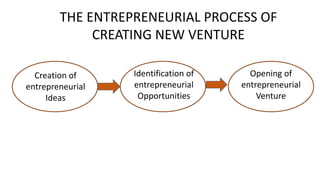
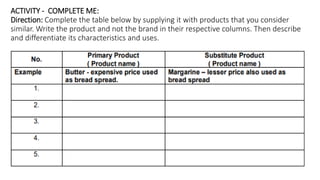
Here are some examples of completing the table with substitute products:
Product 1 Product 2
Description and differentiation
Soda Pop Beer
Both are carbonated beverages but soda pop is non-alcoholic while beer contains alcohol. Soda pop is commonly consumed as a refreshment while beer is an alcoholic beverage.
Bread Pasta
Both can be used as a staple food but bread is made from wheat while pasta is made from grains like wheat and rice. Bread is soft while pasta has different shapes. Bread is commonly used for sandwiches while pasta is often served with sauce.
Pen Pencil
Both can be used for writing but a pen uses liquid ink while a pencil uses graphite. A pen provides