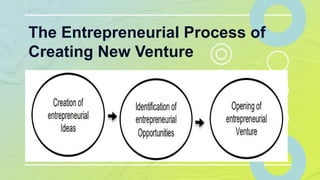
The document outlines a lesson on recognizing potential markets and seeking entrepreneurial opportunities. It covers identifying market needs, proposing solutions, and understanding the role of an entrepreneur in addressing these needs through creativity and awareness of external factors. Key elements include the sources of opportunities such as changes in the environment, technological advancements, government policies, people's interests, and past experiences in the industry.