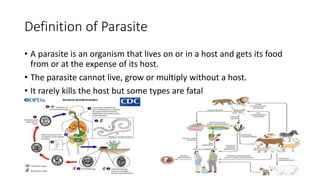
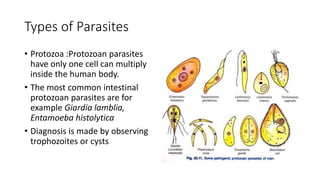
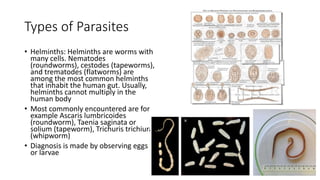
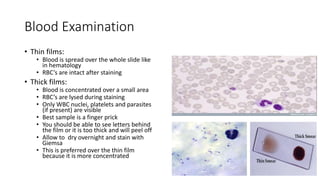
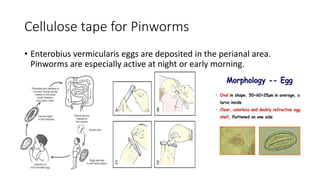
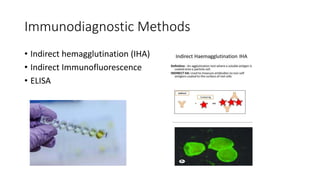
This document discusses parasites, including their definition, diagnosis, transmission, types, and methods of examination. It defines a parasite as an organism that lives on or in a host and gets its food from the host. Parasites are diagnosed through patient symptoms, travel history, and examining samples like stool, blood, or tissue under a microscope. Transmission depends on factors like sanitation, diet, geography, and reservoirs. Common parasite types are protozoa like Giardia and helminths like roundworms and tapeworms. Samples are examined through wet mounts, concentration methods, staining, and immunological or PCR tests.