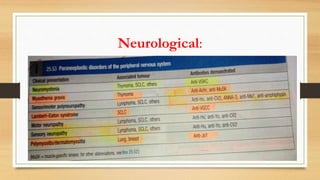
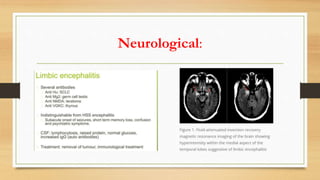
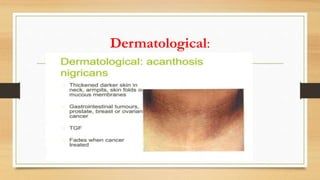
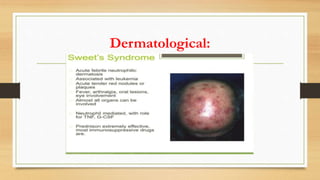
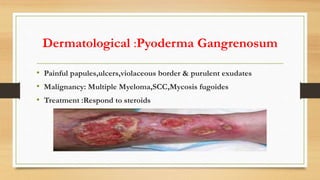
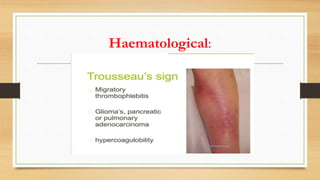
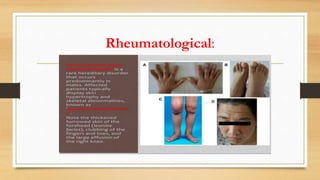
Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare disorders triggered by an altered immune response to cancer. They involve non-metastatic effects that accompany malignant disease. Common types include neurological, endocrine, dermatological, and hematological syndromes. Evaluation involves ruling out other potential causes through testing like bloodwork, imaging, and biopsies to identify underlying cancers. While some symptoms may improve with cancer treatment, paraneoplastic syndromes can also result in irreversible organ damage or progression of cancer.