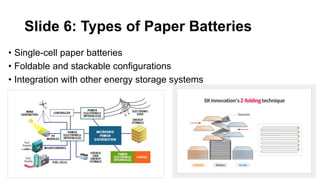
This document discusses paper batteries, which are flexible, ultra-thin energy storage devices formed by combining carbon nanotubes with paper. Paper batteries act as both batteries and supercapacitors. They have advantages like being lightweight, flexible, cost-effective and capable of providing steady or burst energy. Potential applications include portable electronics, medical devices, smart packaging and environmental monitoring. Paper batteries work through the interaction of electrolytes during charging and discharging. They offer potential future power sources due to their flexibility and ability to power devices from something the size of a postage stamp.













![PAPER BATTERY [PPT].pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperbatteryppt-230816130724-b9630c90/85/PAPER-BATTERY-PPT-pptx-15-320.jpg)