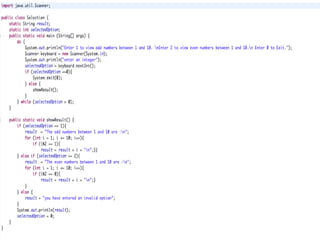
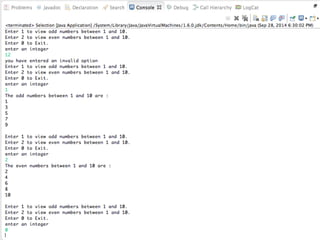
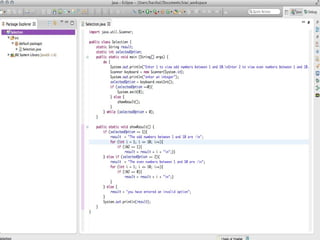
This document provides an introduction to the basics of Java programming language. It discusses Java's history, benefits, shortcomings, and common programs. It also outlines how Java is used in modern applications like mobile operating systems, web development, networking, games, and more. The document covers key topics such as Java being platform independent, object oriented, and its use of classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism.









![GENERAL PROGRAMS
• General java program for hello
class Hello
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(“Hello”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/palash-140929101932-phpapp02/85/PALASH-SL-GUPTA-11-320.jpg)
![GENERAL PROGRAMS
• Program using for loop
class Hello
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
System.out.println(“hello”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/palash-140929101932-phpapp02/85/PALASH-SL-GUPTA-12-320.jpg)
![GENERAL PROGRAMS
• Program using if-else condition
Class Large
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=5,b=7
if(a>b)
System.out.println(“a is large no”);
else
System.out.println(“b is large no”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/palash-140929101932-phpapp02/85/PALASH-SL-GUPTA-13-320.jpg)