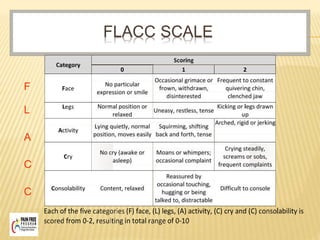
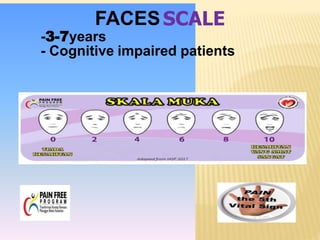
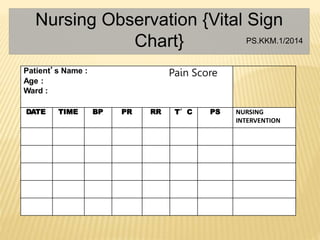
This document discusses pain assessment tools and guidelines. It defines pain as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain should be assessed in all patients as the 5th vital sign using appropriate tools based on a patient's age, such as the FACES scale for children ages 3-7 or the MOH pain scale for adults. Nurses and other medical staff should assess pain at regular intervals, after interventions, and whenever a patient reports pain in order to effectively treat and document pain levels.