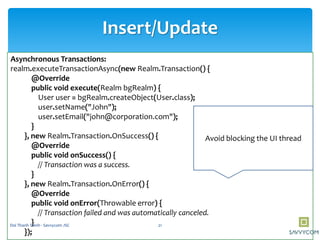
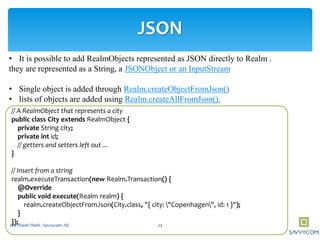
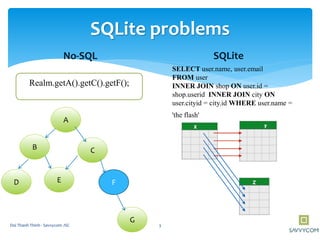
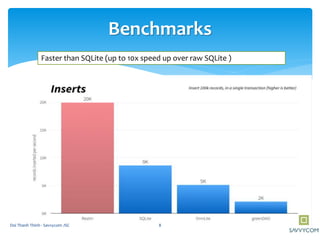
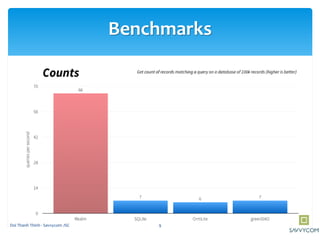
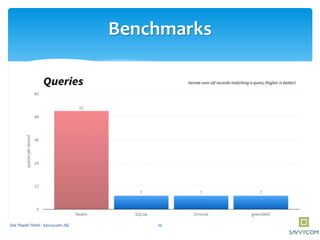
Realm is a mobile database that is faster than SQLite and supports in-memory databases and custom migrations. It can replace SQLite in mobile applications. Realm supports object mapping with models that extend RealmObject and relationships between objects. Queries can be performed on object properties using conditions and sorting. Objects can be inserted, updated, and deleted from Realm asynchronously in transactions to avoid blocking the UI.






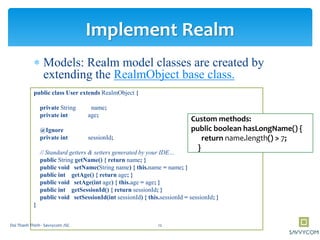
![ Field types:
Supports the following field types:
boolean, byte, short, int, long, float, double, String, Date and
byte[].
The boxed types Boolean, Byte, Short, Integer, Long, Float and
Double
@Required: used to tell Realm to enforce checks to disallow
null values
@Ignore: a field should not be persisted to disk
@PrimaryKey : a primary key field
@Index will add a search index to the field
Implement Realm: Types fields
13Doi Thanh Thinh - Savvycom JSC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentrealm-161129012604/85/Realm-Java-2-2-0-Build-better-apps-faster-apps-13-320.jpg)




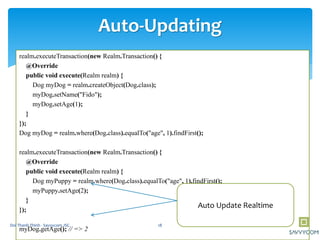
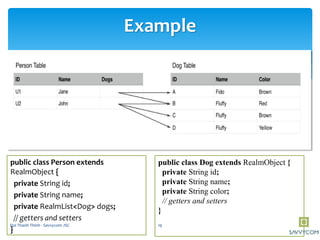
![Example
// persons => [U1,U2]
RealmResults<Person> persons = realm.where(Person.class)
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Brown")
.findAll();
// r1 => [U1,U2]
RealmResults<Person> r1 = realm.where(Person.class)
.equalTo("dogs.name", "Fluffy")
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Brown")
.findAll();
// r2 => [U2]
RealmResults<Person> r2 = realm.where(Person.class)
.equalTo("dogs.name", "Fluffy")
.findAll()
.where()
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Brown")
.findAll();
.where()
.equalTo("dogs.color", "Yellow")
.findAll();
20Doi Thanh Thinh - Savvycom JSC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentrealm-161129012604/85/Realm-Java-2-2-0-Build-better-apps-faster-apps-20-320.jpg)