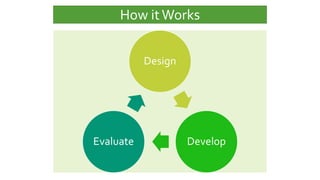
Rapid prototyping is an iterative design process where initial design ideas are quickly represented in a working online prototype with minimal time and resources. The prototype tool should be able to represent the interactivity of the final product and allow for easy adjustments. Prototypes should take no more than an hour to create. Rapid prototyping allows designers to quickly fix problems, emphasizes evaluation, and accommodates changing needs through faster user feedback. However, it can fail without proper analysis and designs may become uncontrolled.