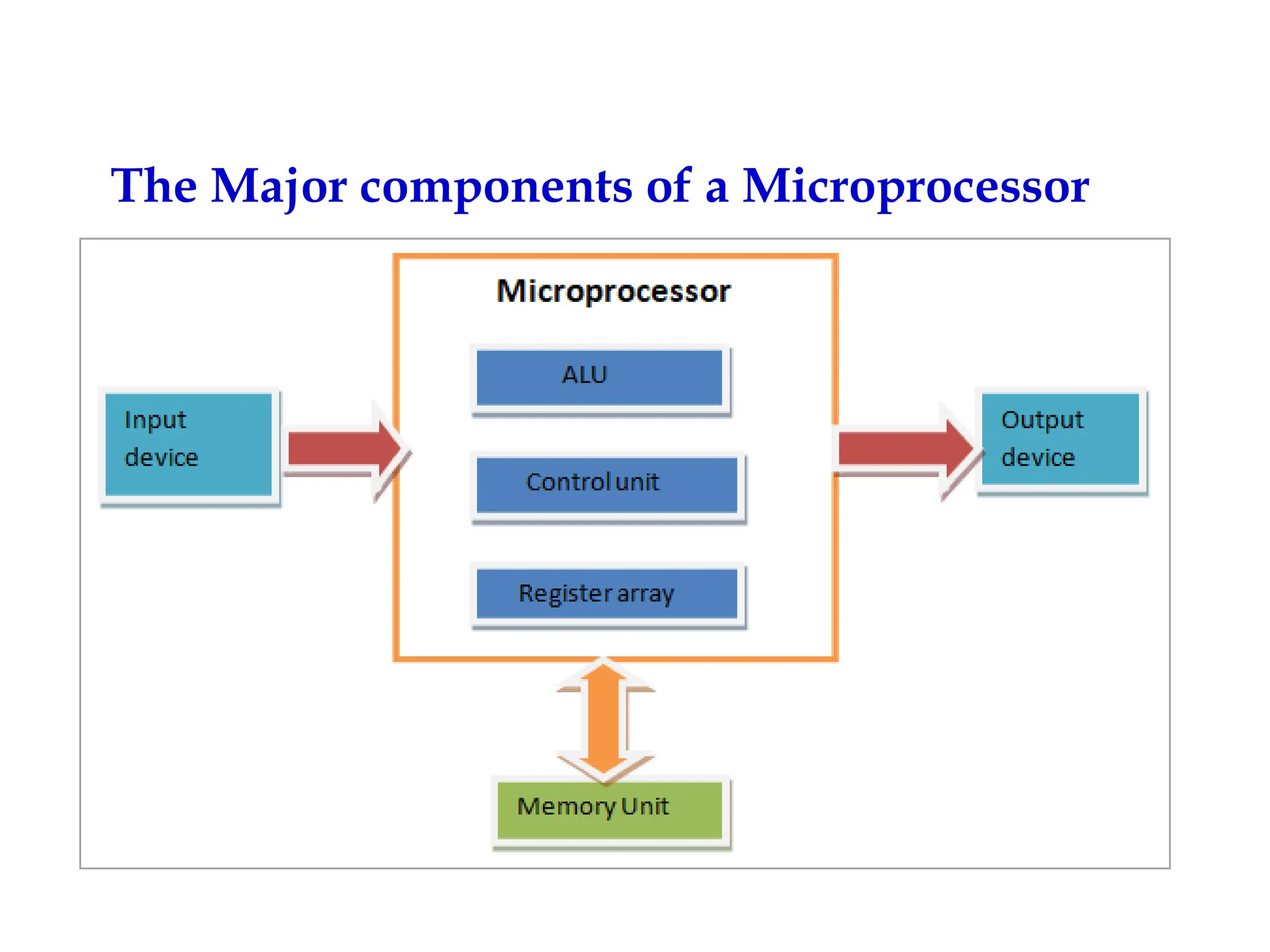
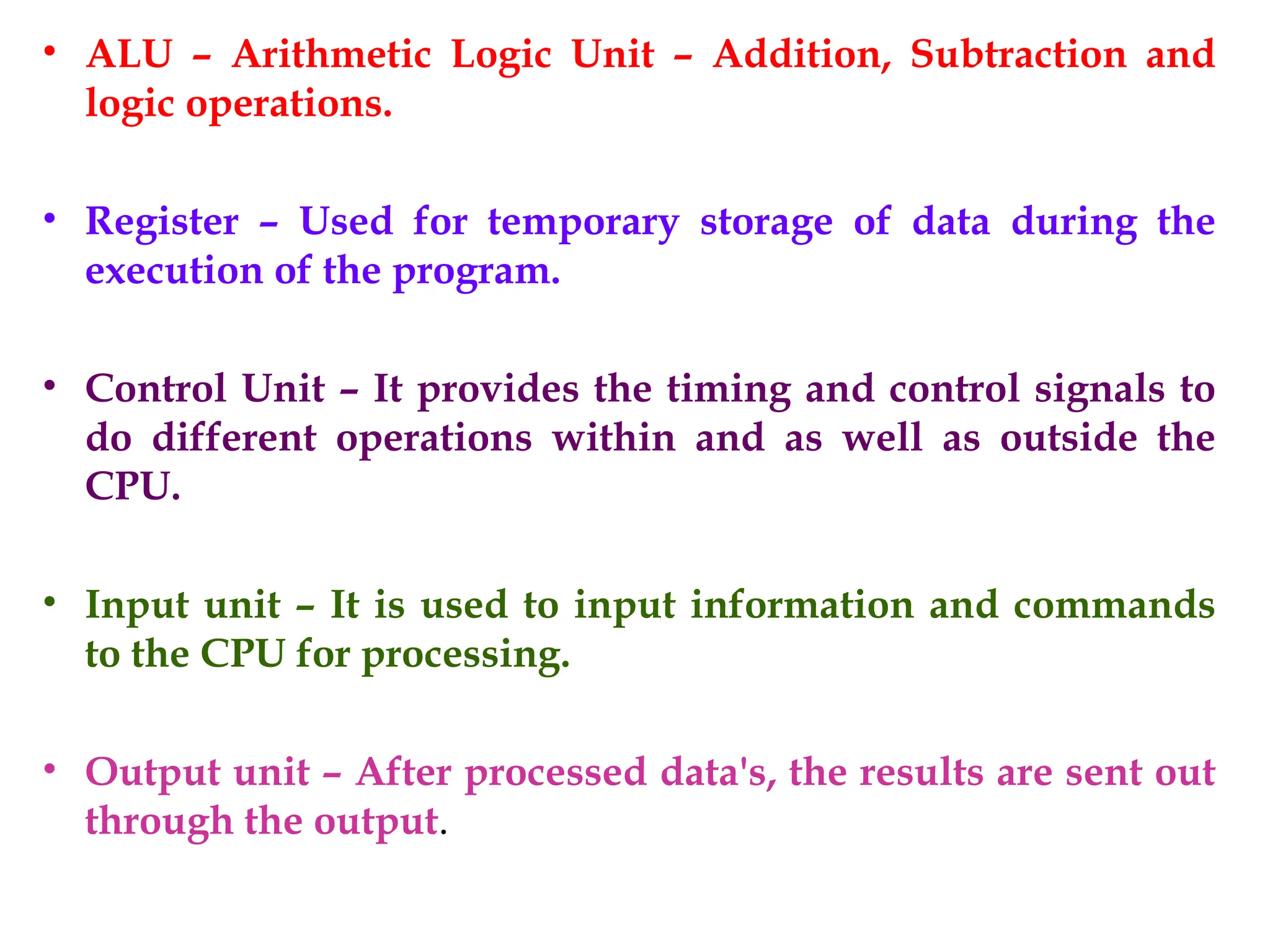
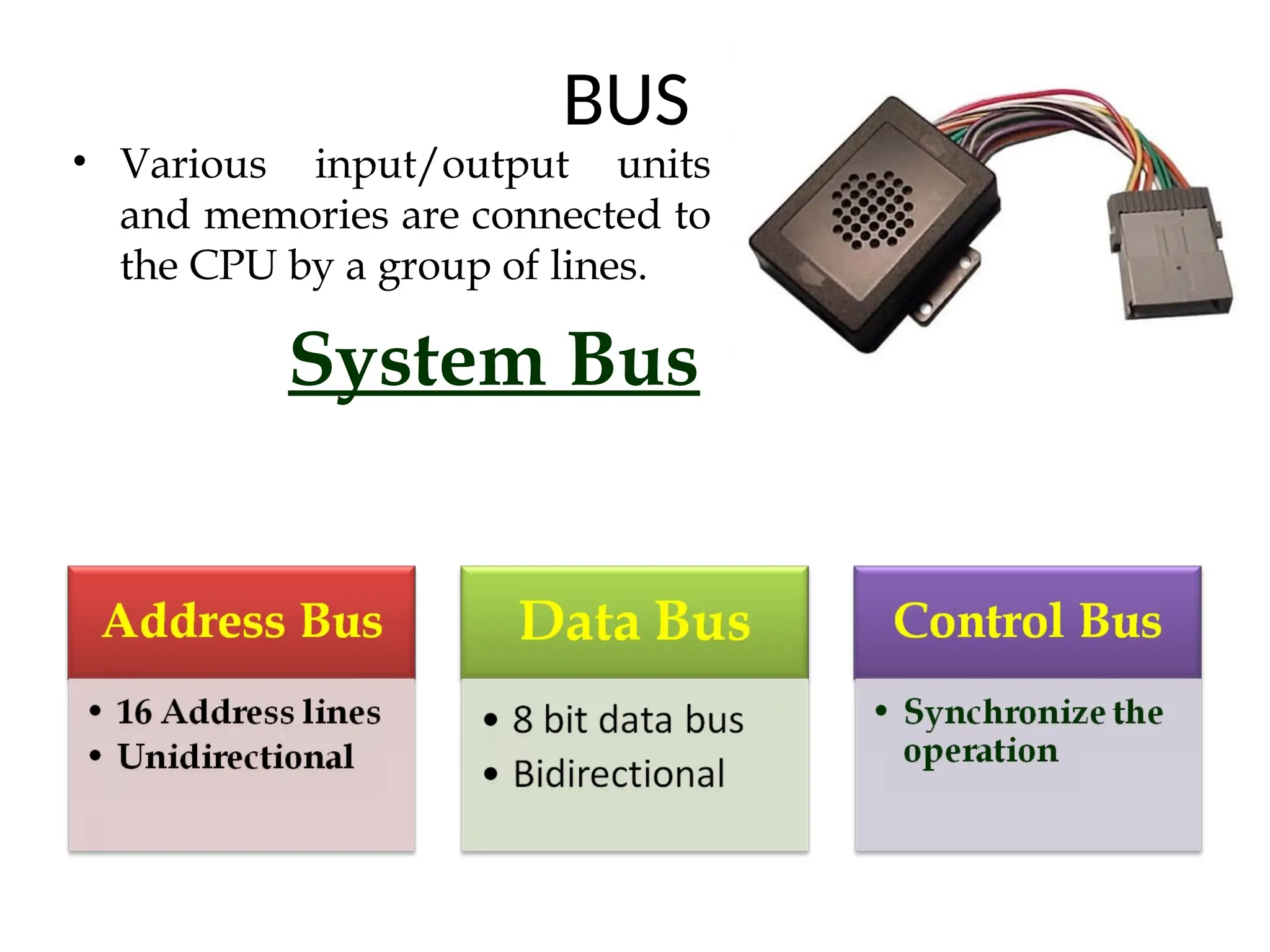
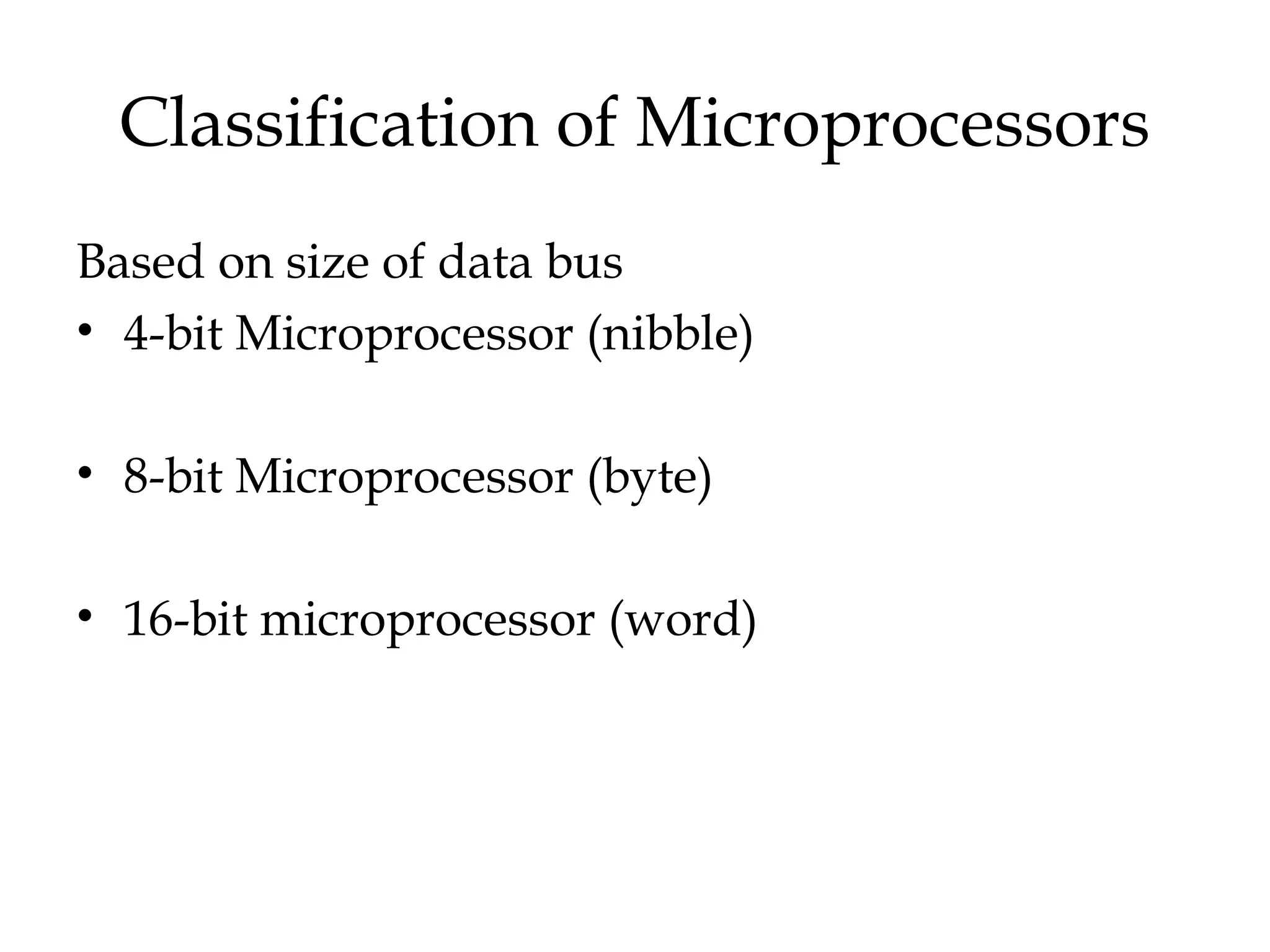
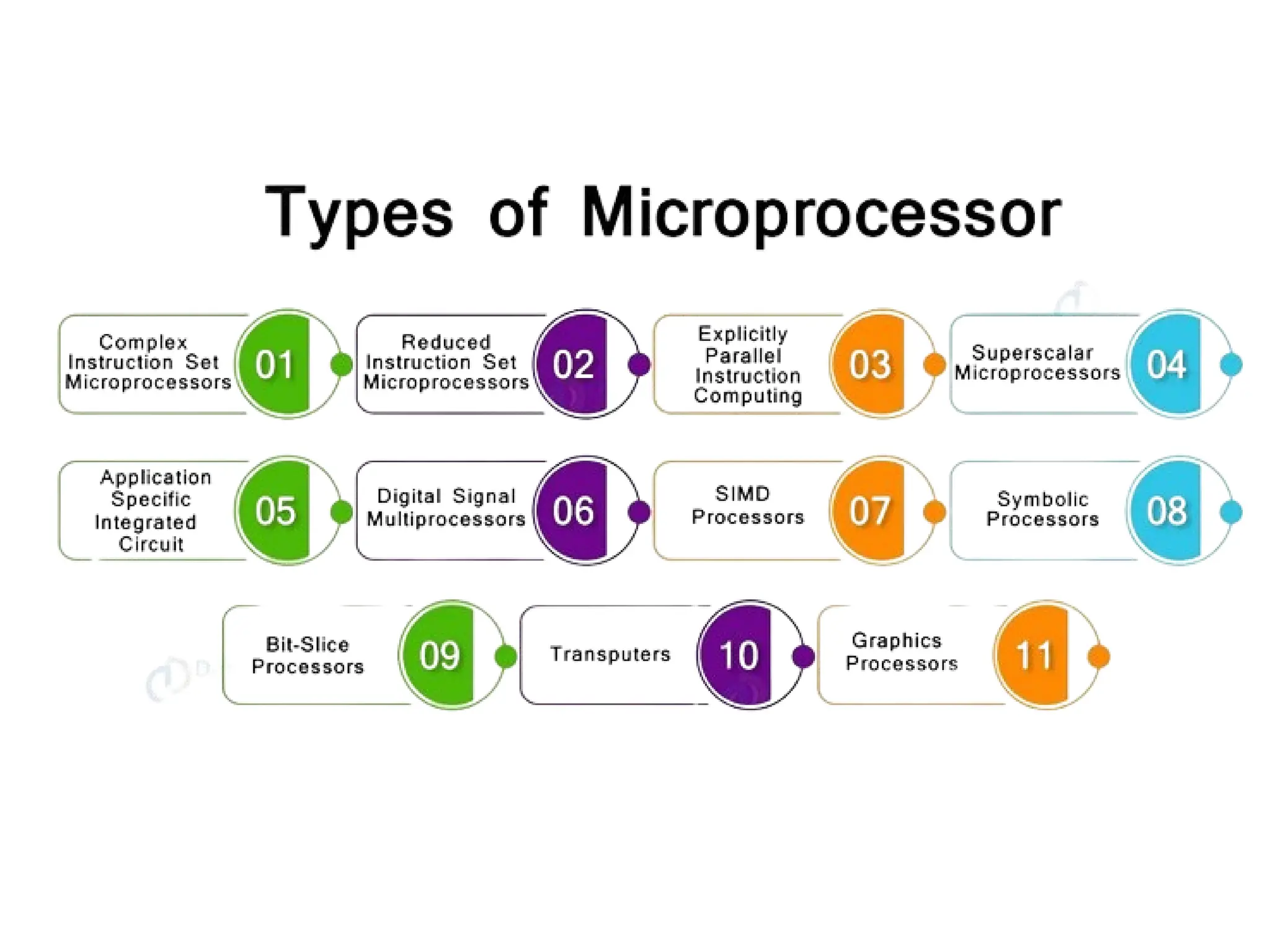
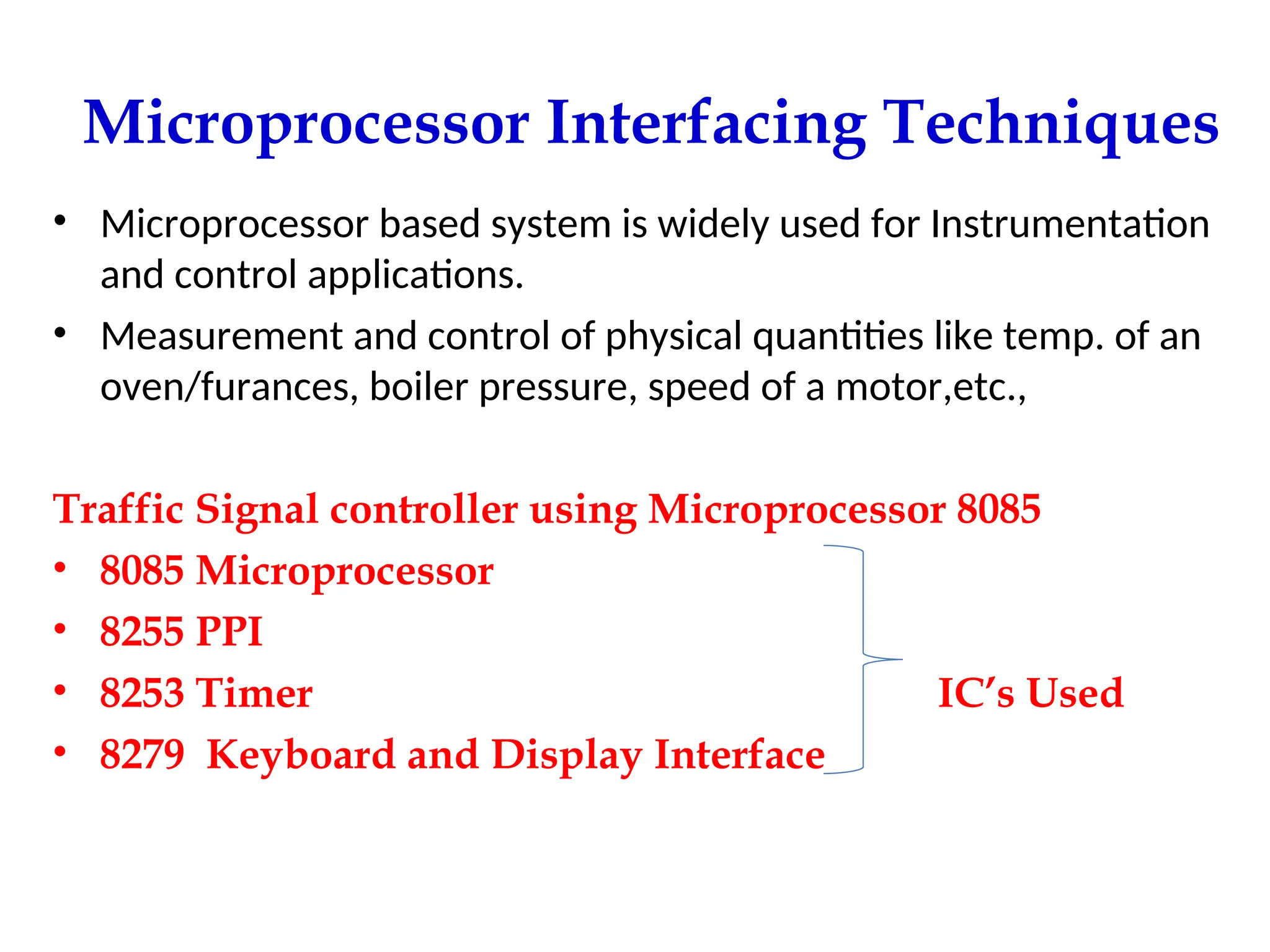
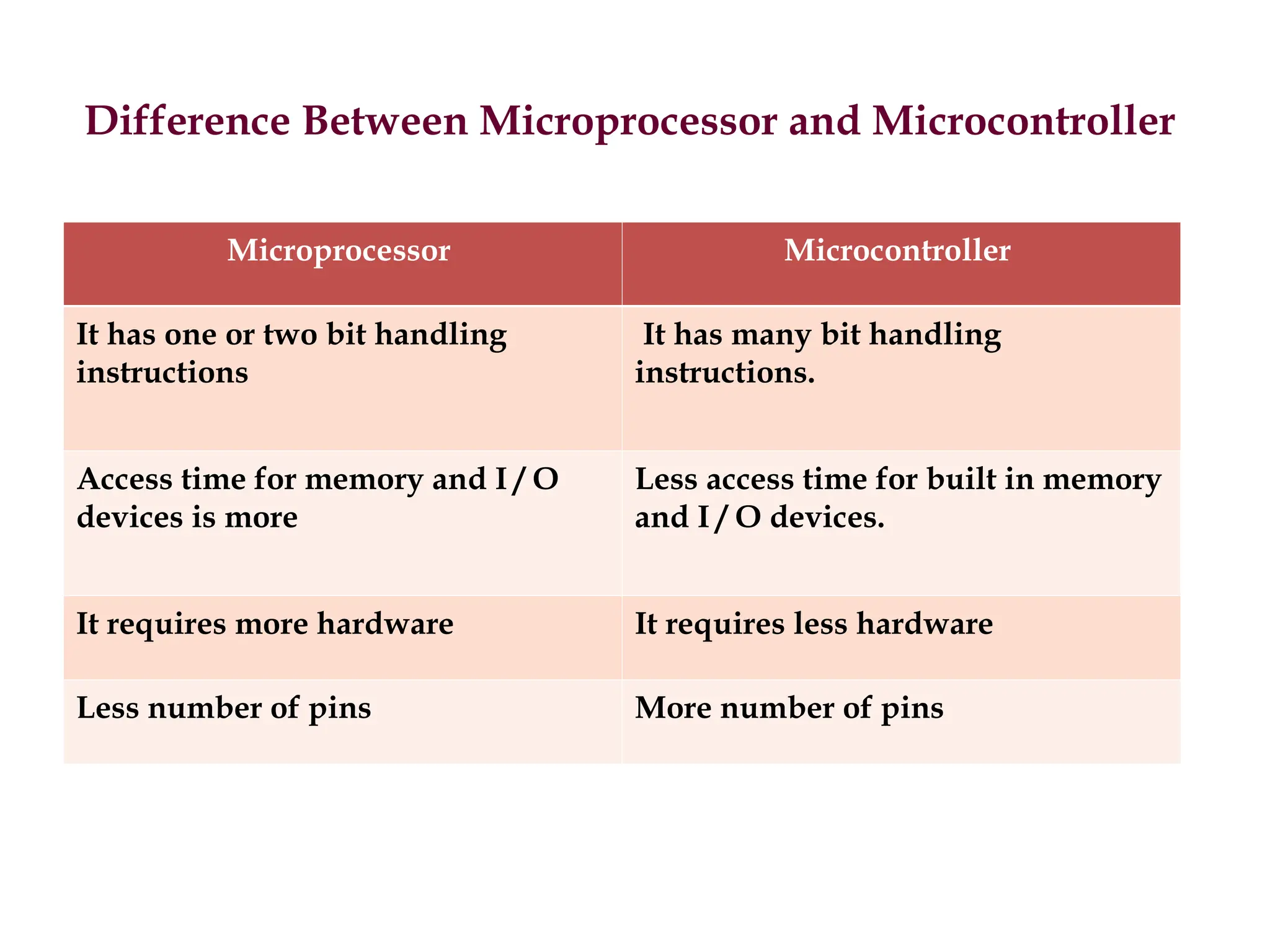
The document provides a comprehensive overview of microprocessors, detailing their evolution, features, and components, alongside the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers. It highlights significant milestones in microprocessor history, including the introduction of various Intel models from 1971 onwards, and discusses key internal components such as the ALU and control unit. Additionally, it covers interfacing techniques and applications, emphasizing the role of microprocessors in instrumentation and control systems.