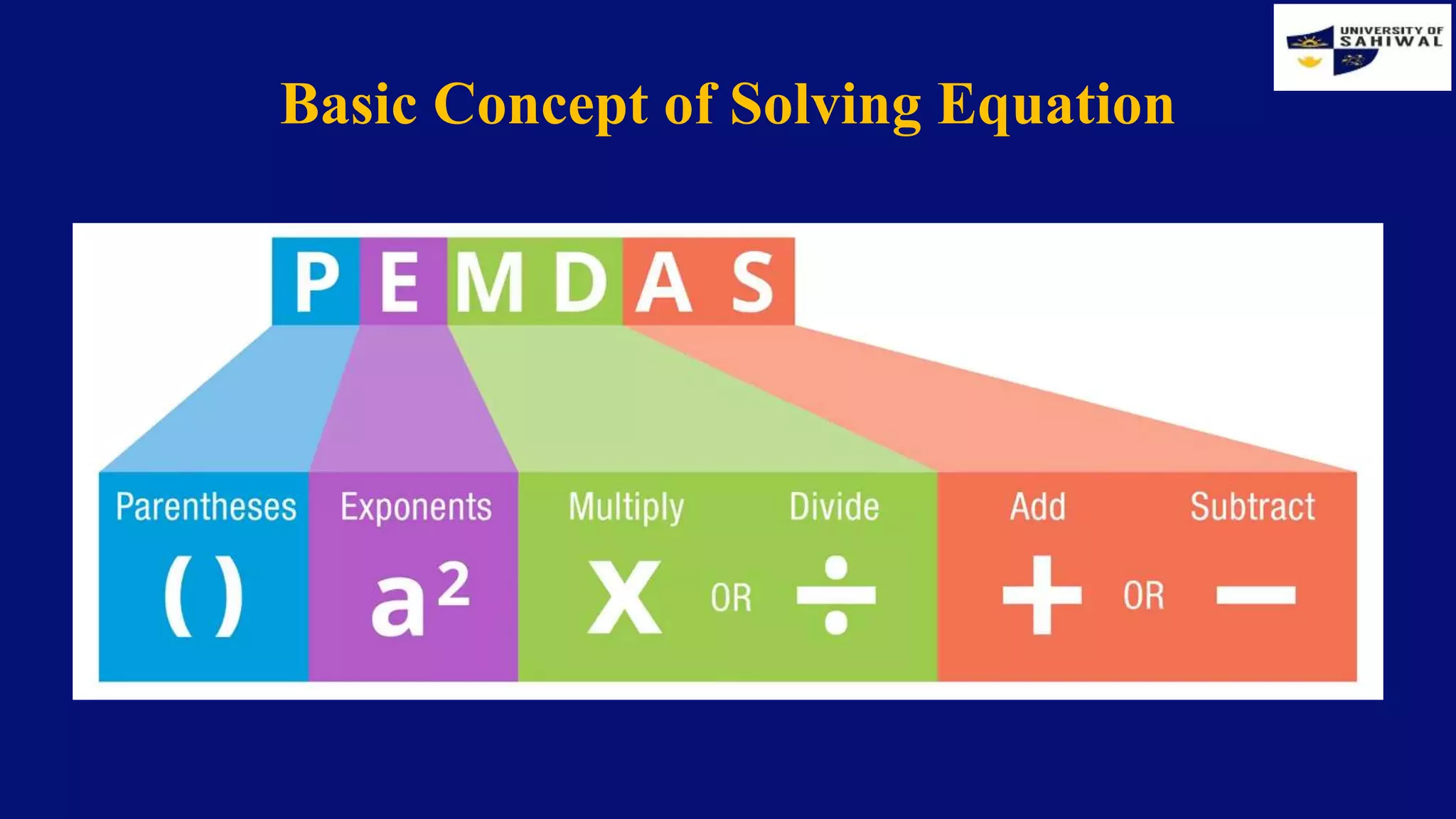
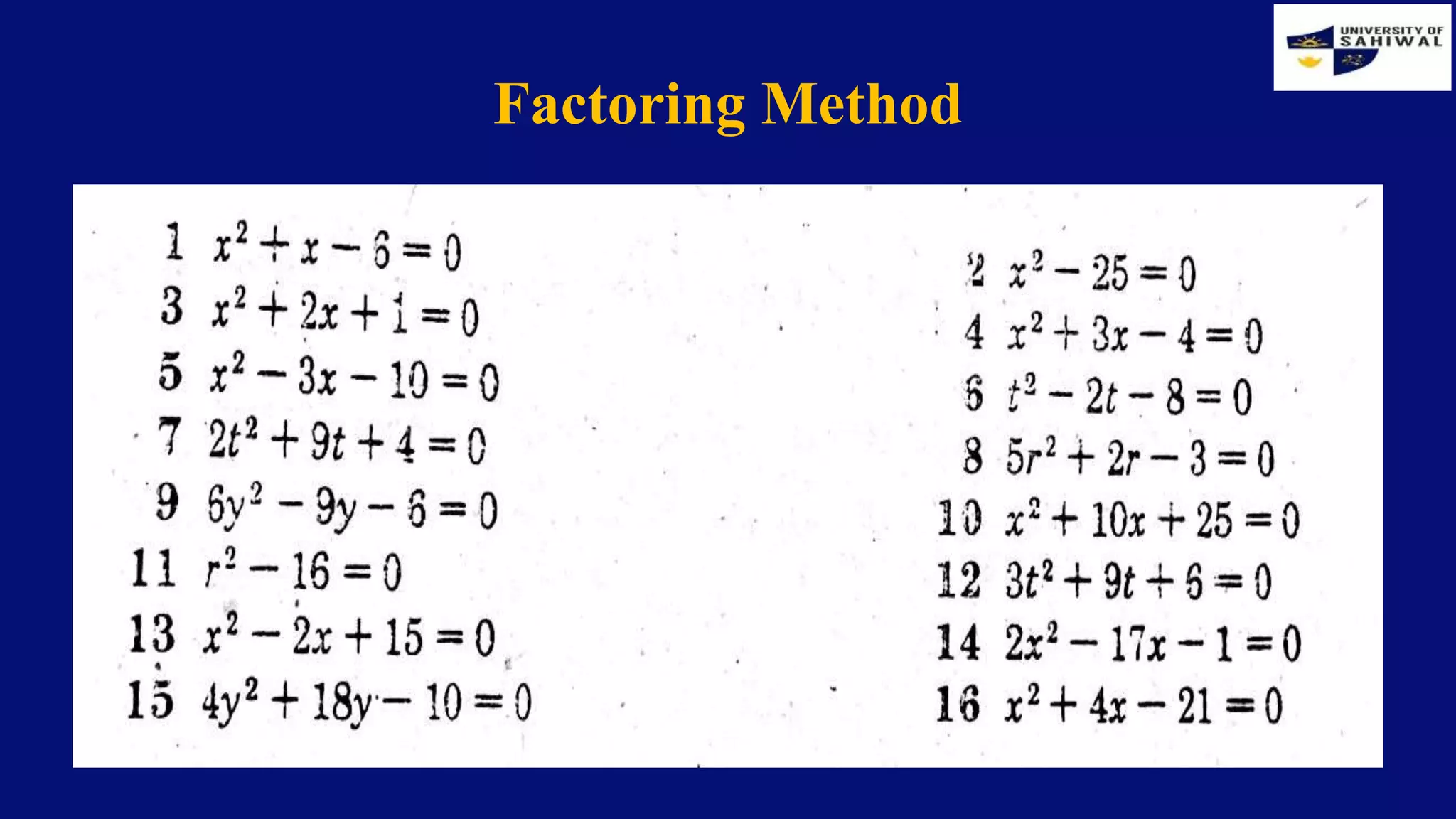
This document provides an overview of business mathematics and some preliminary concepts. It discusses what business math is and how it is used in various business departments and daily life. Some key applications include accounting, finance, and calculating revenues and costs. The document also introduces a PUPP problem-solving model and covers solving first and second degree equations, including using factoring and the quadratic formula. Exercises and examples are provided to illustrate solving different types of equations.