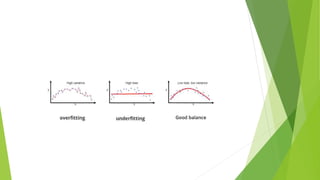
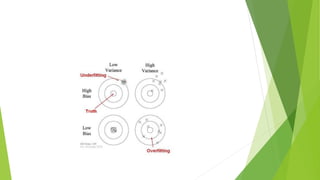
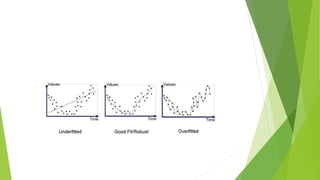
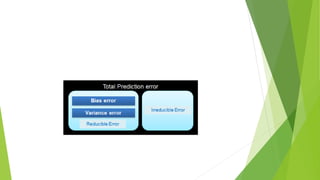
Bias is the difference between a model's predicted values and the correct values being predicted. Models with high bias oversimplify the data and have high error rates. Overfitting occurs when a model learns the noise in addition to the underlying patterns in the training data, resulting in low bias but high variance. Underfitting happens when a model cannot capture the underlying patterns due to being too simple, resulting in high bias but low variance. The bias-variance tradeoff aims to balance a model's complexity to avoid underfitting and overfitting.