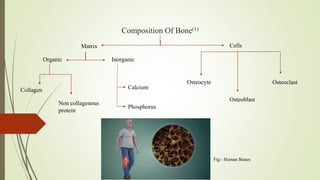
The document discusses molecular mechanisms of osteoporosis. It defines osteoporosis as a medical condition where bones become brittle and fragile from loss of tissue, often due to hormonal changes or deficiencies in calcium or vitamin D. The document outlines that bones are composed of an organic matrix and inorganic minerals including calcium, phosphorus, and collagen. It also describes the roles of osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts in bone formation and resorption. Pathways involved in osteoporosis pathogenesis include glucocorticoid signaling and molecular signals such as RANKL, DKK-1, and sclerostin. Treatments discussed are antibody therapies targeting these molecules as well as stem cell therapy and