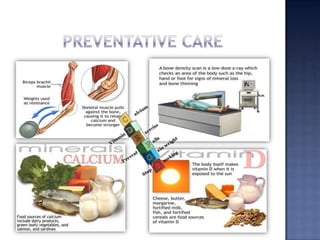
Osteoporosis is a disease where bone density and mass decreases over time, making bones thin and brittle. It is the most common bone disease, affecting 1 in 5 American women over 50. Risk factors include lack of estrogen, smoking, excessive alcohol, family history, and low calcium intake. Symptoms may include bone pain, loss of height, fractures from minor falls or injuries. Treatment focuses on exercise, adequate calcium and vitamin D, and medications to rebuild bone density and prevent fractures.