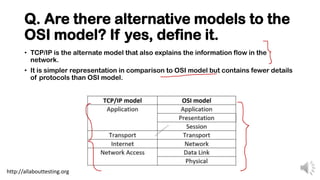
The document discusses the OSI model, which consists of seven layers that facilitate understanding of information flow in networking, though it does not perform functions itself. It compares the OSI model with the simpler TCP/IP model, outlines differences between TCP and UDP protocols, and explains the importance of the physical layer. Additionally, it covers network problem detection, error detection and recovery functions, data encapsulation, and the distinction between half-duplex and full-duplex communications.